Dismantling Joints: Detailed Technical Information

Table of Contents
ToggleEverything You Need to Know About Dismantling Joints: Detailed Technical Information, Types, Usage Areas, and Materials
Dismantling joints play a crucial role in connecting and gathering detailed technical information for various applications in the plumbing and piping industry. These joints are designed to provide easy access to different types of pipes and facilitate maintenance and repairs. They come in various sizes, materials, and lock types to accommodate different usage areas and technical requirements. Understanding the detailed technical data, types, usage areas, and materials of dismantling joints is essential for professionals in the plumbing and piping industry.
Understanding Dismantling Joints
Dismantling joints play a crucial role in simplifying the installation and replacement of flanged fittings in retrofitting applications. These joints provide a practical solution for adding, repairing, or replacing flanged fittings within a flanged pipe system. Their adjustable, slip joint designs can accommodate wide gaps or close-quarter installations and eliminate the need for precise measurements between flange connections. Dismantling joints are available in sizes 2″ and larger, suitable for use in ductile iron or flanged PE piping systems.
Definition and Functionality
Dismantling joints are essential components in piping systems, offering the flexibility to dismantle and reassemble flanged pipe components such as valves, pumps, and meters. Their primary function is to assist in the easy removal and installation of these components for maintenance or replacement purposes. By providing a convenient way to separate and reconnect flanged pipe segments, dismantling parts minimize the need for extensive cutting or welding, reducing downtime and labor costs during maintenance activities.
Components of a Dismantling Joint
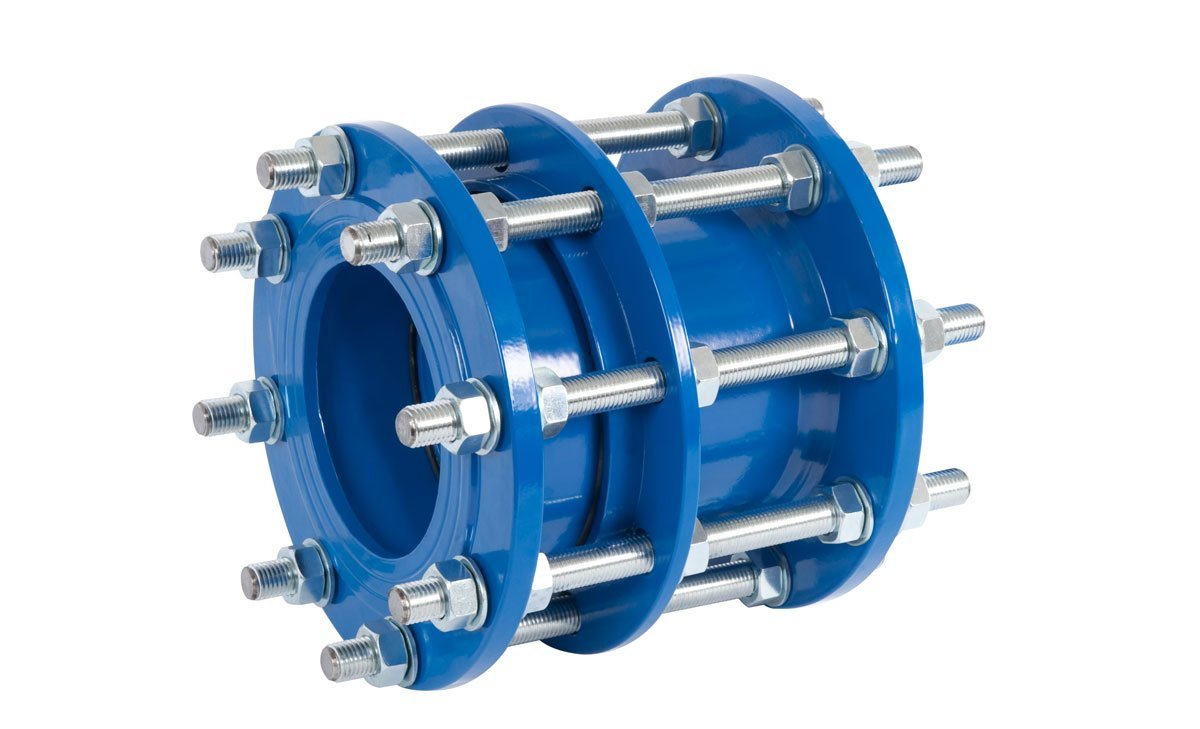
Dismantling joints typically consist of several key components, including:
- Flanged Ends: These ends are designed to connect to the existing flanged pipe components, ensuring a secure and leak-free attachment.
- Central Sleeve: The central sleeve acts as a pivotal point, allowing for the movement and adjustment of the joint to accommodate varying distances between flanged pipe segments.
- Tie Rods: These rods provide structural support and maintain the alignment of the joint during operation, ensuring stability and reliability.
- Gaskets: Gaskets are crucial for creating a tight seal between the dismantling joint and the connected flanged components, preventing leakage and ensuring efficient fluid flow.
Overall, dismantling joints are engineered to facilitate the efficient disconnection and reconnection of flanged pipe segments, enabling seamless maintenance and repair operations within piping systems.
7 Benefits of Using Dismantling Joints on Valve and Pipeline Systems
When it comes to valve and pipeline systems, the use of dismantling joints can offer a wide range of benefits that contribute to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the system. Whether it’s for maintenance, repair, or installation purposes, these joints play a crucial role in ensuring that the system operates smoothly and seamlessly.
Dismantling joints offer several advantages that make them a preferred choice in piping systems, including ease of installation and maintenance, as well as flexibility and adaptability. Here are some of the 7 key benefits of using dismantling joints on valve and pipeline systems:
7 Main Advantages of Dismantling Joints
- 1Flexibility and AdaptabilityDismantling joints provide the flexibility to accommodate various pipe materials, sizes, and misalignments, allowing for easier installation and adjustments. This adaptability reduces the need for custom-made components, making the system more versatile and cost-effective.
- 2Streamlined Maintenance and RepairsWith dismantling joints, maintenance and repairs become more manageable and efficient. These joints allow for the easy removal and reinstallation of valves and other pipeline components, minimizing downtime and reducing the overall cost of maintenance.
- 3Stress Reduction on Piping SystemBy absorbing and distributing the forces caused by thermal expansion, vibration, and other external factors, dismantling joints help reduce stress on the piping system. This not only extends the lifespan of the system but also enhances its overall safety and reliability.
- 4Enhanced Sealing and Leak PreventionDismantling joints contribute to improved sealing of the pipeline system, reducing the risk of leaks and ensuring better containment of fluids or gases. This is particularly crucial in industries where fluid leakage can lead to environmental or safety hazards.
- 5Simplified InstallationWhen installing new pipeline systems or making modifications, dismantling joints simplify the process by allowing for easier alignment and connection of pipes and valves. This streamlined installation process saves time and labor costs while ensuring a precise and secure fit.
- 6Mitigation of Corrosion and ErosionThe use of dismantling joints can help mitigate the impact of corrosion and erosion on the pipeline system. By facilitating easier access for inspection and maintenance, these joints contribute to the early detection and prevention of potential issues, ultimately prolonging the system’s lifespan.
- 7Compliance with Industry StandardsDismantling joints play a role in ensuring that valve and pipeline systems comply with industry standards and regulations. By providing a mechanism for proper alignment and connection, these joints contribute to the overall integrity and safety of the system.
In conclusion, the benefits of using dismantling joints on valve and pipeline systems are undeniable. From enhancing flexibility and adaptability to simplifying maintenance and repairs, these joints are integral to optimizing the performance and longevity of the entire system. By understanding and leveraging the advantages they offer, industries can maximize the efficiency and reliability of their valve and pipeline infrastructure.

FAQ: Importance of Dismantling Joints on Pipeline Systems
Dismantling joints play a critical role in the design and layout of valves and pipelines. They allow for longitudinal adjustment, making it possible to precisely insert and remove pipe valves and sections. This flexibility facilitates rapid installation and removal, increasing efficiency and reducing downtime.
Dismantling joints enable quick installation and removal of pipe valves and sections, reducing downtime and site operations. They also allow for rapid installation of pipe sections and valves without causing restraint in flexible pipelines. Additionally, dismantling joints can fill gaps, such as connecting a pump installation to a pipe protruding from a wall.
The basic design principles of dismantling joints include a flange adaptor securely joined to the pump or valve, a flanged spigot with a flange at the other end for connection, and the ability to install or remove valves with longitudinal adjustment. The joints also utilize a high-quality rubber gasket to ensure a leak-tight system.
Dismantling joints allow for the precise insertion and removal of valves by providing longitudinal adjustment. This adjustment enables the valve to be fitted next to the dismantling joint at the accurate length needed before being securely connected to flanges. When removing a valve, readjusting the dismantling joint’s length creates enough space to loosen and remove the valve.
Dismantling joints simplify pipeline maintenance and repair by allowing for the rapid installation and removal of pipe valves and sections. This contributes to increased efficiency and reduced downtime during maintenance and repair operations.
Types of Dismantling Joints
Flanged Type Dismantling Joints
Flanged type dismantling joints are designed with flanges at both ends, providing a simple means of disassembling and reassembling the pipeline. These joints are particularly useful in applications where there is a need for frequent maintenance or where the pipeline may need to be dismantled for repairs or replacements. The flanges allow for easy and quick removal of the joint, making it an efficient solution for various pipeline systems.
Mechanical Joint Dismantling Joints
Mechanical joint dismantling parts feature a mechanical connection, which allows for easy installation and removal without the need for welding. This type of joint is often used in water and wastewater systems, as well as in industrial piping applications. The mechanical joint design provides flexibility and ease of maintenance, making it a popular choice for infrastructure projects.
Restraint and Non-Restraint Variants
Dismantling joints come in both restraint and non-restraint variants, offering different levels of movement restriction. Restraint variants are designed to restrict axial movement, providing stability and support to the pipeline. Non-restraint variants, on the other hand, allow for flexibility and movement, making them suitable for applications where some degree of movement is anticipated. The choice between restraint and non-restraint variants depends on the specific requirements of the pipeline system, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
In summary, the various types of dismantling joints, including flanged type, mechanical joint, and restraint/non-restraint variants, offer versatility and adaptability for different pipeline systems, addressing the need for maintenance, repair, and movement accommodation.
Specifications and Technical Data
Pressure Ratings and Size Ranges
Pressure ratings for dismantling joints vary based on the specific model and manufacturer, but typically range from 16 bar to 25 bar, accommodating a wide range of applications. Size ranges also vary, with options available to suit pipe diameters from 80mm up to 2000mm, ensuring flexibility in diverse piping systems. Understanding the pressure ratings and size ranges is crucial for selecting the appropriate dismantling part for a given application, guaranteeing optimal performance and safety within the system.
Weight Considerations for Installation
When considering the installation of dismantling joints, the weight of the joint plays a critical role in the overall handling and installation process. Depending on the material and design, dismantling joints can weigh anywhere from a few kilograms to significantly heavier weights, necessitating appropriate lifting and handling equipment. Ensuring that the weight considerations are factored into the installation process helps in preventing any safety hazards and ensures the successful integration of the dismantling part within the piping infrastructure.
Materials Used in Dismantling Joints
Dismantling joints are crucial components in piping systems, designed to facilitate the rapid disassembly of flanged pipe connections. This section will explore the various materials used in the construction of dismantling parts, with a focus on common materials, durability, and coatings for corrosion protection.
Common Materials and Durability
Dismantling joints are typically constructed using robust materials to ensure longevity and performance in demanding environments. Common materials used in their fabrication include ductile iron, stainless steel, carbon steel, and coated steel. Ductile iron, known for its high tensile strength and impact resistance, is widely favored for its durability and reliability in conveying fluids under high pressure.
Stainless steel is another popular choice due to its corrosion resistance properties, making it suitable for applications involving aggressive or corrosive substances. Carbon steel, valued for its strength and versatility, is often employed in dismantling parts to withstand varying operating conditions. Additionally, coated steel, such as fusion-bonded epoxy (FBE) or polyethylene, is utilized to enhance the durability and corrosion resistance of dismantling joints, particularly in underground installations exposed to soil or moisture.
Coatings and Corrosion Protection
To mitigate the effects of corrosion and extend the service life of dismantling joints, various coatings are applied to the surfaces. Fusion-bonded epoxy (FBE) coatings, known for their exceptional adhesion and resistance to chemicals and moisture, provide a protective barrier against corrosion, making them ideal for applications in aggressive environments.
Similarly, polyethylene coatings offer superior resistance to abrasion and chemicals, safeguarding dismantling parts from corrosive elements present in the fluid conveyed. These coatings play a crucial role in preventing premature degradation and maintaining the structural integrity of dismantling joints, ensuring reliable performance over an extended period.
Usage Areas of Dismantling Joints
Water and Wastewater Systems
Dismantling joints play a crucial role in water and wastewater systems, where they are used to facilitate efficient maintenance and repair operations. By providing a flexible and convenient connection between pipelines, dismantling parts allow for easy disassembly and reassembly without the need for extensive excavation or disruption to the overall infrastructure. In the context of water and wastewater systems, dismantling joints are instrumental in ensuring the seamless operation and longevity of pipelines, enabling swift access for inspection, maintenance, and potential repair work.
Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, dismantling joints are employed to support various applications, including but not limited to industrial pipework, chemical processing facilities, and power generation plants. Their ability to accommodate angular and axial movement makes them invaluable components in industrial piping systems, allowing for efficient maintenance and repair activities without the need for extensive shutdowns or disruptions to critical operations. Dismantling parts contribute to the overall reliability and integrity of industrial pipelines, enabling seamless access and adaptability for a wide range of maintenance and operational requirements.
Installation Guidelines for Dismantling Joints
Pre-Installation Checks
Before commencing the installation process of dismantling parts, it is crucial to conduct a thorough inspection of the product. This includes checking the packaging and visual examination to ensure there is no damage from transportation and no missing parts. Additionally, it is essential to verify that the flange to which the dismantling joint will be fitted matches the bore of the product flange and that the nominal pressure is consistent.
Step-by-Step Installation Process
- Remove Pull Rod Bolts: Begin by removing the pull rod bolts from the dismantling joint. Loosen the nut and take the pull rod bolts so that the pipe moves freely in the body of the flange connection.
- Position Dismantling Joint: Move the dismantling joint between the flanges to be assembled. Ensure there is an O-ring gasket between the flanges for sealing. Use flange bolts to secure the flange end of the dismantling joint and fix the flange end which needs to be attached. Tighten the bolts securely.
- Connect Flange Spigot: Connect the flange spigot to the opposite mating flange. Place flange type O gaskets between the flange faces and bolt them together with flange bolts.
- Self-Sealing of Dismantling Joint: After the bolts connect the flange, self-sealing of the dismantling joint should be put into the program. Apply lubricant in the middle of rubber seals to ensure that the intermediate flange and intermediate sealing ring slide to the location. Verify the small self-connection bolt gasket and nut.
- Insert Pull Rod Bolts: Insert the pull rod bolts. Each rod has 4 nuts at assembly. When the pull rod is inserted, connect the bolt with the nut. The pull rod bolt the connector is equal to meet the requirements of the flanges at both ends. Tighten the other nut on the joint after tightening the rod nut to complete the installation.
- Ensure Proper Tightening: Evenly press the bolt on the press in the alternating direction of the screw until it reaches the recommended torque. Wait for ten minutes and then torque.
Common Installation Problems
- The bolt is not tight enough to meet the required torque.
- Small debris between seals or gaskets.
- Dirt on bolts or nuts causing problems with nut fastening.
- The short distance inserted by the spigot pipe.
- Incorrect mating flange.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Routine Inspection and Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance of the dismantling joint is crucial in ensuring its optimal performance and longevity. Start by conducting visual inspections for any signs of wear, such as corrosion, leaks, or irregularities in the joint’s components. Check for loose bolts and ensure that the joint’s sealing surfaces are clean and free from debris. Additionally, lubricate moving parts as per the manufacturer’s guidelines to prevent friction-related issues. It is recommended to schedule routine maintenance based on the joint’s usage and environmental conditions.
Common Issues and How to Address Them
One common issue with dismantling joints is leakage, often caused by damaged gaskets or improper installation. To address this, inspect the gaskets for any signs of wear or deterioration and replace them if necessary. Another issue may arise from misalignment, leading to stress on the joint during operation. Ensure proper alignment and consider using flexible couplings to mitigate misalignment issues. Additionally, if there are issues with bolt tightness, perform a torque check and re-tighten as needed, following the manufacturer’s specifications. Regularly monitor the joint’s performance to identify and address any emerging issues promptly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dismantling joints are crucial components in piping systems, allowing for easy maintenance and repair. They come in various types, such as lock type and different pressure ratings to suit specific requirements. These joints are made from durable materials like cast iron or ductile iron, ensuring longevity and reliability in various usage areas. By gathering detailed technical information about dismantling joints, including dimensions, weight, and pressure ratings, engineers and industry professionals can make informed decisions about their usage in pipeline installations and maintenance.