The Impact of Corrosion on Plug Valve Performance

Table of Contents
ToggleMaximizing Plug Valve Longevity and Performance: Navigating the Impact of Corrosion
Corrosion in plug valves is a critical consideration for engineers and technical staff seeking to optimize the performance and longevity of these essential components. Whether in chemical processing, oil and gas, or other industrial applications, the detrimental effects of corrosion on plug valves can lead to significant operational and safety concerns. It’s vital to address the impact of corrosion to ensure the reliability and durability of lubricated and non-lubricated plug valves.
The gradual deterioration caused by corrosion can compromise the structural integrity of plug valves, leading to potential leaks, diminished functionality, and costly downtime. By understanding the importance of corrosion resistance and implementing effective maintenance and protection strategies, engineers can mitigate the risks associated with corrosion and safeguard the long-term performance of the valves in various operational environments.
In this blog post, we will delve into the specific challenges posed by corrosion in plug valves, explore the key factors influencing their longevity and performance, and provide valuable insights into the preventative measures and technologies that can enhance corrosion resistance.
Whether you’re tasked with the maintenance, troubleshooting, or selection of plug valves, gaining a comprehensive understanding of the impact of corrosion is essential for ensuring the reliability and optimal functionality of these crucial components in industrial processes.
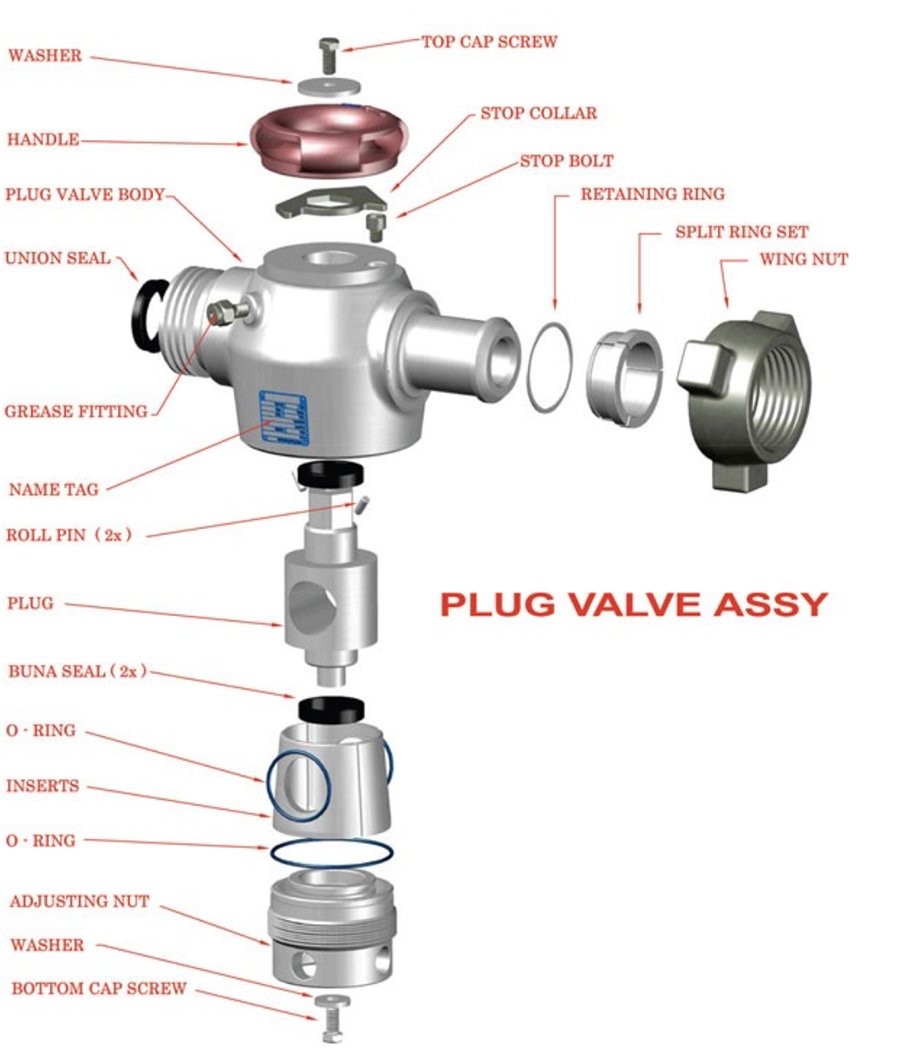
Understanding Plug Valve Corrosion
Corrosion is a significant concern when it comes to the longevity and performance of plug valves.
It can lead to decreased efficiency and potential safety risks if not properly addressed. Understanding the causes and types of corrosion in the valves is crucial for engineers and technical staff to effectively manage and mitigate these issues.
Causes of Corrosion
Chemical Exposure
Chemical exposure is a common cause of corrosion in plug valves, especially in industrial settings where valves come into contact with aggressive chemicals. The reaction between the chemicals and the valve material can lead to degradation and corrosion over time.
High Temperatures
Elevated temperatures can accelerate the corrosion process in plug valves. The combination of high temperature and chemical exposure can further exacerbate the corrosion, leading to potential failure of the valve components.
Abrasive Media
The presence of abrasive media flowing through plug valves can cause erosion-corrosion, where mechanical wear and chemical corrosion occur simultaneously, resulting in accelerated material loss.
Environmental Conditions
Environmental factors such as humidity, moisture, and atmospheric pollutants can contribute to corrosion in plug valves, particularly in outdoor or coastal environments where exposure to salt and moisture is prevalent.
Types of Corrosion
Uniform Corrosion
Uniform corrosion occurs evenly across the surface of the valve material, leading to a gradual thinning of the material. While it may not cause immediate failure, prolonged uniform corrosion can compromise the structural integrity of the valve.
Pitting Corrosion
Pitting corrosion results in the formation of localized pits or holes on the valve surface. These tiny cavities can penetrate deep into the material, reducing its strength and potentially causing leaks or ruptures in the valve.
Stress Corrosion Cracking
Stress corrosion cracking can occur in plug valves exposed to tensile stress in corrosive environments. It is characterized by the formation of cracks, often leading to sudden and catastrophic failure of the valve components.
Understanding the specific causes and types of corrosion in plug valves is essential for implementing effective preventive measures and selecting appropriate materials and coatings to mitigate the impact of corrosion on valve longevity and performance.

Impact on Longevity and Performance
Corrosion has a significant impact on the longevity and performance of plug valves, affecting their structural integrity and functional reliability. Understanding the specific ways in which corrosion influences valve operation is crucial for engineers and technical staff involved in maintenance and operations.
Degradation of Valve Materials
Corrosion leads to the degradation of plug valve materials, compromising their structural integrity and overall functionality. In lubricated plug valves, the presence of corrosive media can accelerate the breakdown of internal components, such as valve seats and seals. This can result in leakage and reduced operational efficiency, ultimately affecting the longevity of the valve.
Similarly, non-lubricated plug valves are susceptible to corrosion-induced material degradation, particularly in aggressive environments. The exposure to corrosive substances can lead to erosion of the valve body and internal components, compromising their mechanical properties and long-term performance.
Understanding the specific vulnerabilities of materials used in plug valves, such as stainless steel, alloy metals, and specialized coatings, is essential for mitigating the effects of corrosion and ensuring the extended longevity of these critical components in industrial applications.
Effect on Internal Components
Corrosion significantly impacts the internal components of plug valves, leading to reduced sealing efficiency and increased friction within the valve assembly.
The accumulation of corrosion products on sealing surfaces can impede proper closure and create leakage paths, resulting in diminished operational reliability.
In addition, the increased friction caused by corroded internal components can lead to operational challenges, including difficulty in actuation and potential damage to valve mechanisms. Real-world performance issues, such as loss of flow control, increased pressure drop, and impaired shut-off capability, are direct consequences of corrosion affecting the internal components of the valves.
By addressing the impact of corrosion on the internal workings of plug valves, engineers and technical staff can implement proactive maintenance strategies and material selection criteria to enhance the resilience of these critical components in demanding industrial environments.
Preventive Measures and Maintenance Strategies
When it comes to ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of plug valves, implementing preventive measures and maintenance strategies is crucial. By proactively addressing corrosion issues, the reliability and efficiency of the valves can be significantly enhanced, leading to cost savings and operational continuity.
Protective Coatings and Linings
Protective coatings and linings play a pivotal role in safeguarding plug valves from corrosion in various operating environments. By applying specialized coatings, such as epoxy, fluoropolymer, or ceramic linings, the susceptibility of the valves to corrosive substances can be mitigated. Different operating conditions, including high temperatures, abrasive media, or corrosive chemicals, may necessitate the use of specific coating materials to ensure comprehensive protection.
For lubricated plug valves, the application of resilient coatings to internal components can help reduce friction and wear, thereby prolonging the valve’s service life. Non-lubricated plug valves can benefit from corrosion-resistant coatings that serve as a barrier against corrosive elements, preserving the structural integrity of the valve components.
Maintenance Best Practices
Implementing robust maintenance best practices is essential for detecting and addressing corrosion-related issues in the valves. Regular inspection and monitoring of key components, including the valve body, sealing surfaces, and operating mechanisms, are paramount in identifying early signs of corrosion or wear. Visual and non-destructive testing methods can be employed to assess the condition of critical areas and prioritize maintenance interventions.
Furthermore, incorporating scheduled lubrication routines for lubricated plug valves and periodic seal replacements for both lubricated and non-lubricated types are fundamental in preventing accelerated corrosion and maintaining sealing integrity.
Establishing a comprehensive cleaning and flushing protocol can aid in removing debris and contaminants that may contribute to corrosion initiation or propagation within the valve assembly.
By adhering to meticulous maintenance practices, technicians and engineers can effectively mitigate corrosion risks and uphold the longevity and performance of plug valves across diverse industrial applications. Regular maintenance not only ensures the operational reliability of plug valves but also contributes to overall system integrity and safety.
By integrating protective coatings, thorough maintenance, and proactive strategies, the detrimental impact of corrosion on plug valve longevity and performance can be mitigated, facilitating sustained operational efficiency and minimizing unplanned downtime.
Case Studies and Industry Insights
Corrosion mitigation in plug valves is a critical concern for engineers and technical staff worldwide. Successful case studies and industry insights shed light on effective strategies and emerging technologies that have reshaped the approach to combating corrosion in these valves.
Successful Corrosion Mitigation
Several successful corrosion mitigation initiatives have extended the longevity and improved the performance of plug valves. For instance, cathodic protection offers a mechanism to control external corrosion by making the valve’s surface the cathode of an electrochemical cell. Additionally, the selection of corrosion-resistant materials, non-metallic materials, and metal surface treatments have proven effective in preventing and mitigating corrosion in the valves.
In a specific case study, a plug valve suffered from corrosion due to the presence of chlorides. The implementation of standard Electroless Nickel Plating (ENP) provided a cost-effective and efficient solution to protect the valve against corrosion, particularly in the presence of chlorides. This approach extended the valve’s longevity and enhanced its performance, showcasing the effectiveness of tailored corrosion mitigation strategies.
Innovative Solutions and Technologies
The industry is witnessing a paradigm shift in combating corrosion in plug valves through innovative solutions and emerging technologies. Advanced techniques such as thermal spraying have emerged as a promising approach to protect valves from corrosion.
The use of innovative materials and coating technologies, including valve coating and lining, has significantly enhanced the resistance of the valves to corrosive environments, thereby extending their longevity and boosting performance.
Moreover, the integration of materials with higher resistance to corrosion and erosion has revolutionized the design and manufacturing of these valves. Industry trends reflect a growing emphasis on research and development aimed at enhancing materials and design to address the challenges posed by corrosion, positioning plug valves at the forefront of reliability and longevity in various applications.
Corrosion mitigation in plug valves is constantly evolving, presenting engineers and technical staff with a dynamic landscape of successful initiatives and innovative technologies to safeguard valves against the detrimental effects of corrosion.
As the industry continues to embrace technological advancements and best practices, the pursuit of effective corrosion mitigation strategies remains pivotal in ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of valves in diverse operating conditions.
Conclusion
In summary, the impact of corrosion on plug valve longevity and performance is significant. Corrosion and erosion due to media or environmental conditions can lead to degradation of the valve material, affecting its reliability and lifespan. To ensure reliable operation, engineers and technical staff must prioritize proactive measures and ongoing maintenance.
Implementing regular inspections, cleaning, and the use of protective coatings can significantly extend the lifespan of plug valves and enhance their performance in diverse applications. By prioritizing maintenance, professionals can mitigate the effects of corrosion and ensure the optimal functionality of plug valves over time.