Lug vs. Wafer Butterfly Valves: Comparing Performance
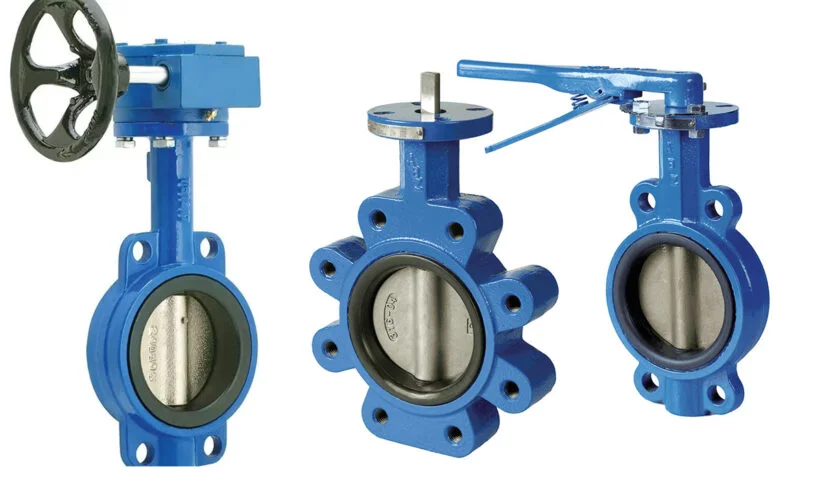

Table of Contents
TogglePerformance Evaluation: Lug vs. Wafer Butterfly Valves
The lugged vs wafer butterfly valve comparison highlights significant differences in their installation processes due to their unique design features. Wafer butterfly valves have a “wafer-thin” design, making them a cost-effective solution for systems with space constraints. They are installed between two pipeline flanges, with bolts tightening the flanges together to secure the valve in place.
However, this design does not allow for isolation during maintenance, requiring the entire system to be shut down. In contrast, lugged butterfly valves have threaded inserts at both ends, allowing independent disconnection of each side of the pipeline without disrupting the other side. This feature makes lugged butterfly valves an excellent choice for systems that require regular maintenance or need to accommodate changes in pressure or flow. Therefore, while wafer butterfly valves are ideal for compact systems with minimal maintenance needs, lugged butterfly valves are better suited for larger, more complex systems where maintenance and system flexibility are crucial.
Lug vs. Wafer Butterfly Valves
When it comes to selecting the right butterfly valve for a specific application, understanding the differences between lug and wafer butterfly valves is crucial. Both types have their own unique features and applications, and choosing the right one can significantly impact the performance and efficiency of a system.
Lug Butterfly Valve
Lug butterfly valves are designed with threaded inserts or lugs on the valve body. These lugs allow for easy installation and removal of the valve from the pipeline without affecting the rest of the line. The valve can be easily mounted between two flanges using bolts and nuts, providing a secure and robust connection. This design also allows for the isolation of a section of the pipeline for maintenance or repairs without disturbing the rest of the system.
Wafer Butterfly Valve
On the other hand, wafer butterfly valves are designed to fit between two flanges without the need for additional bolts and nuts. This design saves space and is more lightweight compared to lug butterfly valves. Wafer valves are often used in applications where space and weight are critical factors, such as in HVAC systems and low-pressure, air-handling applications. They provide a tight and secure shut-off, making them ideal for applications with limited installation space.
Understanding the unique characteristics of lug and wafer butterfly valves is essential in making an informed decision based on the specific requirements of the system or application. The choice between the two types depends on factors such as pressure, temperature, space availability, weight considerations, and maintenance requirements.
Lugged Butterfly Valves Explained
Design Features of Lugged Butterfly Valves
Lugged butterfly valves are typically composed of durable metals such as ductile iron or steel. They are equipped with threaded tapped lugs strategically positioned on the valve flanges for secure bolt connections. This design feature allows for ease of installation and maintenance, making lugged butterfly valves a reliable choice for various industrial applications.
Installation Process for Lugged Butterfly Valves
The installation process for lugged butterfly valves involves aligning the threaded tapped lugs on the valve flanges with corresponding bolt holes in the pipeline. Once aligned, the bolts are used to secure the valve in place, ensuring a tight and secure fit. Additionally, when used for end-of-line service, it is recommended to incorporate a blind flange for optimal performance.
Advantages of Using Lugged Butterfly Valves
Lugged butterfly valves offer numerous advantages, including versatility in actuation methods such as pneumatic or electric actuation. Moreover, the choice of disc and seat material can be tailored to suit specific application requirements, ensuring efficient flow control and durability. These valves provide a robust and reliable solution for fluid regulation in various industrial settings.
Ideal Applications for Lugged Butterfly Valves
Lugged butterfly valves find ideal applications in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, water and wastewater treatment, food processing, pharmaceuticals, manufacturing, shipbuilding, and HVAC systems. Their adaptability, robust construction, and reliable performance make them well-suited for a wide range of fluid handling operations.

Wafer Butterfly Valves Explained
Design Features of Wafer Butterfly Valves
The design of wafer butterfly valves is characterized by their minimal part count, simple construction, compact size, and light weight. These valves are designed to fit snugly between two pipe flanges without any lugs protruding from the wafer body. The valve body is sandwiched between the pipe flanges, and the body is encircled by the flange bolts. Compared to the lug-style butterfly valves, the wafer style is more cost-effective, preventing the weight of the pipe system from passing through the valve body directly.
Installation Process for Wafer Butterfly Valves
The installation process for wafer butterfly valves involves aligning the valve between the two flanges and securing it in place using lengthy bolts or threaded rods that go straight through the valve’s two flanges. This method of installation pulls the flanges together to hold the valve in place. It is crucial to ensure a strong seal between the valve and the flange connection, which is typically achieved with a rubber or EPDM valve seat.
Advantages of Using Wafer Butterfly Valves
Wafer butterfly valves offer several advantages, including their compact design, lightweight construction, and cost-effectiveness. These valves are suitable for applications where space and weight are critical factors. Additionally, their compatibility with most flange standards and ability to provide a strong seal make them a popular choice for various industrial applications.
Ideal Applications for Wafer Butterfly Valves
Wafer butterfly valves are commonly used in systems designed for unidirectional flow to prevent any backflow. They are specifically designed to maintain a tight seal and protect against bi-directional pressure differentials in liquid flow. These valves are suitable for a wide range of applications, including HVAC systems, water treatment plants, chemical processing, and more. Whether electric or pneumatic actuation is required, wafer butterfly valves are adaptable to meet diverse industry needs.
Pressure Handling Capabilities
Pressure Tolerance in Lugged Butterfly Valves
Lugged butterfly valves are designed to withstand varying degrees of pressure, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. The lugged design provides robust support, distributing the pressure evenly across the valve and the piping system. This feature allows lugged butterfly valves to handle high-pressure environments, making them ideal for industrial settings where pressure differentials are a concern. The secure bolting system in lugged butterfly valves ensures that they can effectively contain and regulate the flow of fluids even under high-pressure conditions.
Pressure Tolerance in Wafer Butterfly Valves
Wafer butterfly valves are renowned for their ability to cope with different levels of pressure. Their compact design and lightweight construction enable them to operate effectively under moderate to high-pressure conditions. The wafer-style configuration allows for a secure seal, preventing leakages and ensuring reliable performance in pressure-sensitive applications. Whether it’s in HVAC systems, chemical processing, or water treatment plants, wafer butterfly valves can maintain their integrity and functionality when subjected to varying pressure levels.
Temperature Variations and Effects
Temperature changes can have a significant impact on the performance of butterfly valves in industrial applications. The response of lugged and wafer butterfly valves to temperature variations plays a crucial role in their effectiveness in controlling the flow of fluids and gases.
How Lugged Butterfly Valves Respond to Temperature Changes
Lugged butterfly valves are designed to withstand temperature variations in industrial processes. The materials used in lugged butterfly valves are carefully selected to ensure resistance to thermal expansion and contraction. The valve’s construction, including the lug support, contributes to its ability to manage temperature changes effectively. As temperatures fluctuate, lugged butterfly valves maintain a reliable sealing performance, ensuring minimal leakage and consistent flow control.
How Wafer Butterfly Valves Respond to Temperature Changes
Wafer butterfly valves are engineered to accommodate temperature fluctuations without compromising their functionality. The design of wafer butterfly valves allows for thermal expansion and contraction without affecting the integrity of the valve’s performance. The materials utilized in wafer butterfly valves are chosen for their thermal stability, ensuring that the valve maintains a secure seal across a range of temperatures. This capability enables wafer butterfly valves to operate effectively and efficiently, even in environments with significant temperature variations.

Performance Comparison
When it comes to butterfly valves, understanding their performance characteristics is essential. Let’s delve into a comparison of pressure and temperature performance, maintenance and durability concerns, and a cost-benefit analysis for lug and wafer butterfly valves.
Comparing Pressure Performance
Lug and wafer butterfly valves differ in their pressure performance. Lug valves provide a higher pressure rating due to their bolted design, making them suitable for applications where higher pressure is a concern. On the other hand, wafer valves offer a lower pressure rating, which is ideal for applications with lower pressure requirements. The choice between the two would largely depend on the specific pressure demands of the system.
Comparing Temperature Performance
When it comes to temperature performance, lug and wafer butterfly valves also demonstrate differences. Lug valves are generally more suitable for handling extreme temperature variations due to their robust construction, making them a preferred choice in applications with fluctuating temperature conditions. Wafer valves, while versatile, may have limitations in extreme temperature environments and are better suited for applications with relatively stable temperature conditions.
Maintenance and Durability Concerns
Maintenance and durability are crucial factors in valve selection. Lug butterfly valves, with their bolted design, offer easier maintenance as they can be removed from the pipeline without affecting the rest of the system. Additionally, their robust construction provides durability, making them suitable for demanding applications. Conversely, wafer valves, while simpler in design, may require more effort for maintenance and may have limitations in terms of durability in comparison to lug valves.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
When evaluating the cost-benefit aspect, both types of butterfly valves have their own merits. While lug valves may have a higher upfront cost due to their robust design, they offer long-term benefits in terms of durability and maintenance ease. Wafer valves, with their simpler design, may have a lower initial cost but could potentially incur higher maintenance expenses over time. Considering the specific operating conditions and long-term maintenance projections is vital in determining the optimal cost-benefit balance.
Understanding the nuances of pressure and temperature performance, maintenance and durability concerns, and the cost-benefit analysis for lug and wafer butterfly valves is essential for making informed decisions in valve selection. Each aspect plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and reliability in diverse industrial applications.
Assessing Your System’s Requirements
When choosing the right valve for your application, it’s crucial to assess your system’s specific requirements. Factors such as flow rate, pressure, temperature, and the type of fluid being handled all play a significant role in determining the most suitable valve for your needs. Understanding these requirements is the foundational step in the selection process.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Valve
- Valve Type and Functionality
- Identify the primary function the valve needs to perform: shut off flow, divert flow, mix flow, pressure relief, backflow prevention, or flow adjustment.
- Choose the appropriate valve type based on its intended function, such as check valves, ball valves, needle valves, or relief valves.
- Material Compatibility
- Ensure that the materials of construction are compatible with the fluids or gases flowing through the system. Consider factors such as chemical resistance and durability.
- Performance Requirements
- Evaluate the temperature and pressure ranges in which the valve will operate. Select materials and designs that can withstand the specific operational conditions.
- Check Valve Special Considerations
- Assess the response time and cracking pressure needed for the check valve to function reliably.
- Consider whether a normally closed or normally open check valve is more suitable based on the system’s typical operation.
By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision when selecting a valve that aligns with your system’s unique operational needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the comparison of performance between pressure and temperature variations in lug and wafer butterfly valves reveals important distinctions. The installation process and design features of these two types play a significant role in their suitability for different system requirements. While wafer butterfly valves are advantageous for compact systems with minimal maintenance needs, lugged butterfly valves offer greater flexibility and convenience for larger, complex systems that require regular maintenance or pressure and flow adjustments. Understanding these differences is crucial for engineers and technicians to make informed decisions when selecting the appropriate butterfly valve for specific system demands.