What is Gate Valve in Plumbing?

Gate Valves in Plumbing: An Essential Guide for Industry Professionals
In the vast landscape of plumbing and fluid control systems, understanding the various components and their functions is crucial for industry professionals. Among these components, the gate valve plays a pivotal role in managing the flow of fluids-such as in plumbing systems. We aim to delve into the technical information surrounding gate valves, elucidating their design, operation, applications, and maintenance practices. By adopting a clear and authoritative tone, this guide aspires to be an invaluable resource for engineers, industry professionals, and valve industry enthusiasts.
What is Gate Valve in Plumbing?
A gate valve, as its name suggests, functions using a gate or wedge that moves perpendicularly to the flow of the fluid. This movement allows the valve to be fully opened or fully closed, offering a clear path or a complete seal within the piping system. Gate valves belong to the family of shutoff valves, making them ideal for on/off control rather than flow regulation.
Key Components and Design
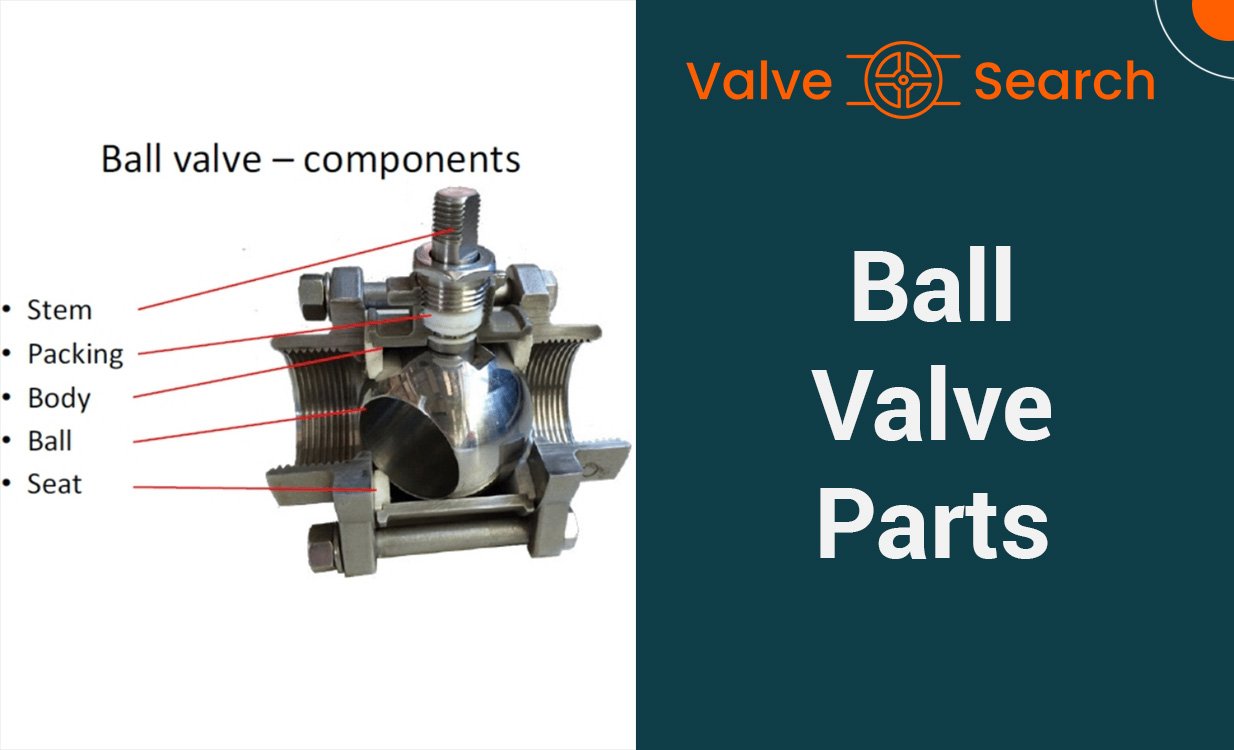
The primary components of a gate valve include the body, which houses the valve mechanisms, the bonnet, which is attached to the body and encloses the moving parts, the gate or disc, the actuator for manual or automatic operation, stem, and the sealing elements which ensure tight closure. These valves are typically made from durable materials like cast iron, stainless steel, or brass, catering to various application requirements.
Operational Insight
Gate valves are celebrated for their simplicity and durability. They operate by the vertical movement of a disk-shaped gate, which aligns with the seats to control the flow path. Unlike other valve types, the linear movement of this valve provides a minimal drop in pressure when fully open, and its tight seal when closed prevents leaks. This operation is facilitated by a handwheel, gear, electric motor, or pneumatic actuator, depending on the valve’s design and intended use.
Applications and Versatility
Given their design characteristics, gate valves are exceptionally suited for applications where a free flow of fluid is necessary, and a full stoppage of flow is required. They are widely used in the water and wastewater management industry, oil and gas pipelines, manufacturing processes, and other areas where fluid control is essential. The choice of gate valve (i.e., material, size, and type) depends heavily on the specific conditions of the application, including pressure, temperature, and the nature of the fluid.
Maintenance Practices
For the durability and dependability of gate valves within plumbing systems, it is imperative to conduct routine maintenance. This includes conducting comprehensive inspections to identify any indications of damage, ensuring that all moving components are adequately lubricated, and swiftly replacing any sealing elements when deemed necessary.
Moreover, it is crucial to take into account the operating conditions, such as extreme temperatures, the existence of corrosive materials, or the presence of particles within the fluid, as these variables can considerably influence the valve’s performance. Therefore, by performing these crucial measures, you can ensure the prolonged functionality of your plumbing system’s gate valves.
Conclusion
For industry professionals, understanding the intricacies of gate valves is crucial for designing efficient and reliable fluid control systems. With their ability to provide a tight seal and regulate the flow of fluids, gate valves are indispensable components in a myriad of applications. By embracing the technical insights and maintenance practices discussed, engineers and enthusiasts can enhance their expertise and contribute to advancements in the valve industry.
In sum, the gate valve, with its straightforward design and effective functionality, continues to be a cornerstone in the field of plumbing and fluid control. It is the clear understanding and proper utilization of such components that drive progress and efficiency within the industry, fulfilling the ever-evolving demands of modern applications.