Main Components of Globe Valves
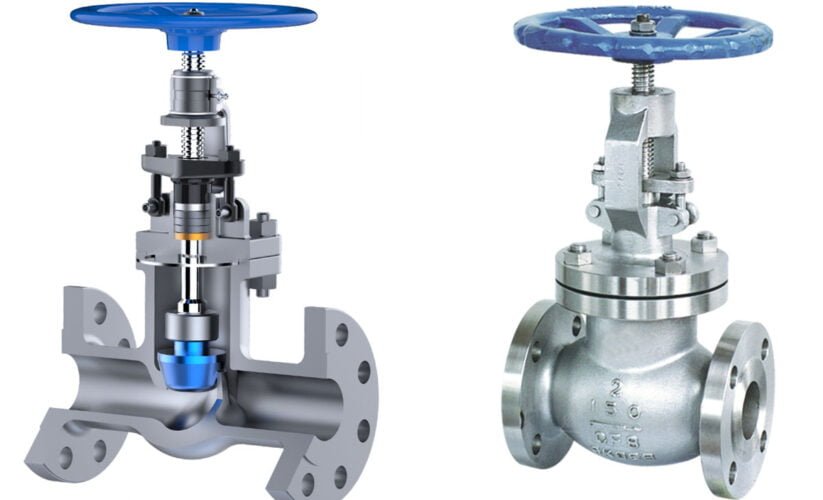

Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Globe valves play a crucial role in controlling the flow of liquids or gases within a pipeline. These valves are commonly used to start and stop fluid flow and to regulate its rate. In this article, we will delve into the fundamental components of globe valves, their functionality, and the different types available in the market. Whether you are new to this subject or seeking a comprehensive refresher, by the end of this read, you will have a clear understanding of components of globe valves and their significance in various industries.
Globe Valves
Globe valves are an essential component in the field of fluid control, offering precise regulation and control. Understanding the design, function, applications and components of globe valves is vital for various industries.
Definition and Function of Globe Valves
Globe valves are linear motion valves used to start, stop, and regulate the flow of fluid. Basic components of globe valves: They consist of a movable disk element and a stationary ring seat, facilitating accurate control of flow rate. The spherical body design allows for efficient throttling of flow and provides a tight seal when fully closed.
Globe valves are particularly suitable for applications requiring fine throttling control and moderate pressure drops. They are commonly used in systems that demand frequent operation and throttling, such as cooling water systems, fuel oil systems, and feedwater systems in power plants.
Applications of Globe Valves in Industry
Globe valves find extensive use across multiple industrial sectors, including oil and gas, petrochemical, pharmaceutical, and power generation. Their ability to offer precise control of fluid flow makes them ideal for applications where regulation and modulation are critical.
In the oil and gas industry, globe valves are utilized in production and refining processes to manage the flow of various fluids and gases. In the power generation sector, they are employed in feedwater control systems and turbine bypass circuits to maintain optimal operating conditions.
The pharmaceutical industry relies on globe valves for their ability to maintain sterility and regulate the flow of liquids and gases in production processes. Additionally, in the petrochemical industry, they play a crucial role in controlling the flow of corrosive and high-temperature fluids.
Industrial processes that require a high level of control and precision benefit from the use of globe valves, making them an indispensable component in fluid control systems.

Main Components of Globe Valves
Globe valves are essential components in fluid control systems, offering precise regulation of flow. Understanding the main components of globe valves is crucial for anyone involved in the design, maintenance, or operation of fluid systems. In this guide, we will delve into the key components of globe valves, shedding light on their functions and importance.
What is the structure of a globe valve?
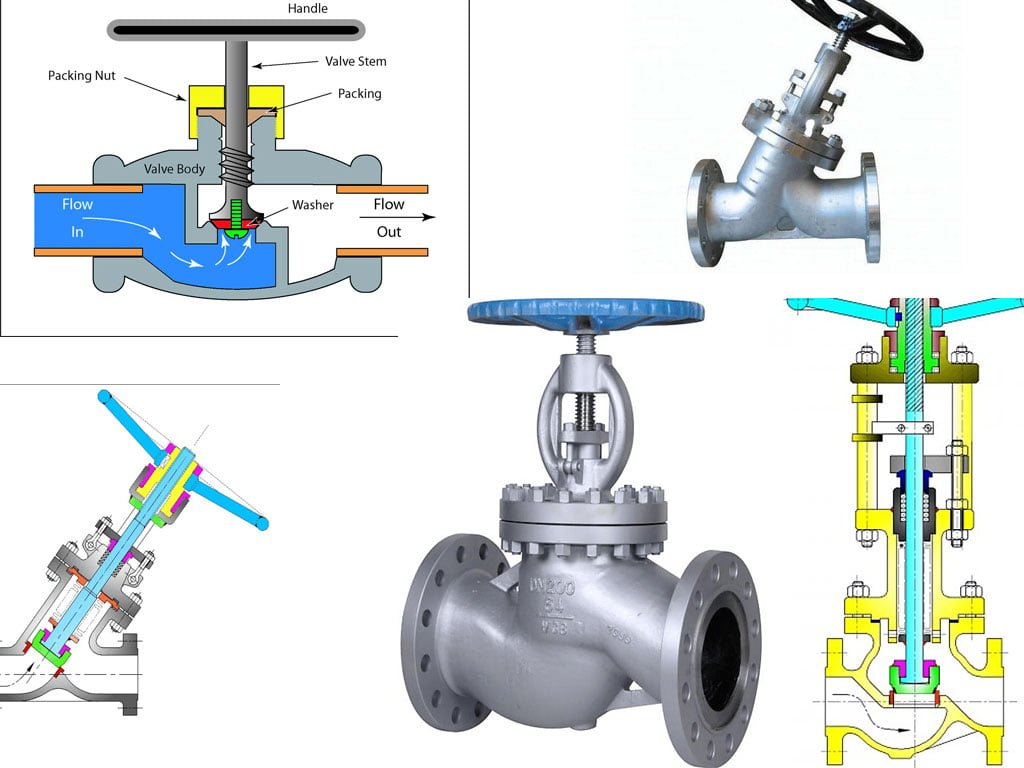
Globe valves have a spherical body shape with two halves separated by an internal baffle. This baffle has an opening that forms a seat onto which a movable plug, also known as a disc, can be screwed in to close the valve.
The valve body in a globe valve serves as the main pressure-retaining part of the valve. It houses other valve parts, including the disc and seat, and allows media to flow in through the inlet and out through the outlet.
Parts / Components of Globe Valves
- Body and Bonnet: The body and bonnet are the main outer casing of the globe valve, providing support and protection for the internal components. They are typically made of durable materials such as cast iron, carbon steel, stainless steel, or bronze, depending on the application and the fluid being handled. The body houses the valve seat and the disc, while the bonnet encloses the moving parts and provides access for maintenance.
- Valve Seat: The valve seat is a crucial component that forms a seal with the valve disc to regulate the flow of fluid. It is often made of resilient materials such as stainless steel, bronze, or synthetic materials to withstand the erosive and corrosive effects of the fluid. The design and material of the valve seat greatly influence the performance and reliability of the globe valve.
- Valve Disc: The valve disc, also known as the plug, is the movable component that controls the flow of fluid through the valve. It is designed to fit into the valve seat, forming a tight seal when closed to prevent leakage. The disc is typically connected to the valve stem, allowing it to be lifted or lowered to regulate the flow of fluid.
- Stem and Actuator: The stem serves as the connection between the valve disc and the actuator, transmitting the force from the actuator to the disc to control the flow. It is essential for the stem to be durable and corrosion-resistant to withstand the operating conditions. The actuator, which can be manual, electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic, provides the necessary force to open or close the valve, allowing for precise control of fluid flow.
- Packing and Gland: Packing is used to create a seal around the valve stem, preventing the leakage of fluid from the bonnet area. It is typically made of materials such as braided graphite, PTFE, or elastomers to provide a reliable and durable seal. The gland, which houses the packing, is designed to apply pressure to the packing, ensuring a tight seal while allowing the stem to move freely.
- Yoke and Stem Nut: The yoke provides support and guidance for the stem, ensuring smooth and stable operation of the valve. It is connected to the bonnet and provides a mounting point for the actuator. The stem nut, often located at the top of the yoke, engages with the threads on the valve stem, converting the linear motion from the actuator into the rotational motion needed to raise or lower the valve disc.
- Handwheel or Handwheel Nut: In manual globe valves, a handwheel or handwheel nut is used to manually operate the valve. It is connected to the stem nut and provides leverage for the user to open or close the valve. The design of the handwheel is crucial for smooth and precise operation, especially in applications where fine adjustments are required.
- Body Bolts and Gaskets: The body bolts are used to secure the body and bonnet together, ensuring a tight and leak-free seal. They are typically made of sturdy materials such as stainless steel and are designed to withstand the forces and pressures exerted on the valve. Gaskets, made of materials such as graphite, PTFE, or rubber, are used to create a seal between the body and bonnet, preventing fluid leakage.
How to Prevent Corrosion on Components of Globe Valves
Corrosion on components of globe valves can lead to decreased efficiency and potential failure of the valve system. Preventing corrosion is crucial for maintaining the functionality and longevity of these essential components. Here are some effective strategies to prevent corrosion on components of globe valves:
Material Selection
Choose corrosion-resistant materials for the construction of globe valve components, such as stainless steel, bronze, or alloy materials with high resistance to corrosion.Protective Coatings
Apply durable and effective protective coatings on the surfaces of globe valve components to create a barrier against corrosive elements, such as epoxy coatings or galvanization.Regular Inspections
Implement a scheduled inspection routine to detect early signs of corrosion on valve components, allowing for timely maintenance and prevention of further damage.Proper Sealing
Ensure proper sealing of the valve components to prevent the intrusion of moisture and corrosive substances that can accelerate the corrosion process.Environmental Control
Control the environment where the globe valves are installed to minimize exposure to corrosive elements, such as moisture, chemicals, or high temperatures.Cathodic Protection
Utilize cathodic protection methods, such as sacrificial anode systems or impressed current systems, to mitigate the effects of corrosion on valve components.Regular Cleaning
Establish a regular cleaning regimen to remove potential corrosive agents from the surfaces of globe valve components, preventing the buildup of corrosive substances.Proper Installation
Ensure proper installation of globe valve components to minimize the risk of exposure to corrosive elements and to maintain the integrity of protective coatings.
By implementing these preventive measures, the components of globe valves can be safeguarded against corrosion, ensuring optimal performance and durability.
Preventing corrosion on components of globe valves is essential for maintaining the efficiency and reliability of these critical industrial elements. By employing proactive strategies such as material selection, protective coatings, regular inspections, and environmental control, the detrimental effects of corrosion can be effectively mitigated, prolonging the lifespan of globe valve components and reducing the risk of operational disruptions.
Conclusion on Components of Globe Valves
Understanding the components of globe valves is crucial for selecting the appropriate valve for your system. Each part, from the bonnet to the stem, plays a significant role in controlling fluid flow. The operation of a globe valve, whether manual or automatic, involves precise movements of the disk to regulate the flow of liquids or gases.
Additionally, the various types of globe valves offer unique advantages based on the specific requirements of a system, making it essential to consider the arrangement and disk type when choosing a globe valve for a particular application. By grasping the intricacies of components of globe valves and their functions, engineers and operators can make informed decisions to ensure efficient and reliable fluid control in diverse industrial settings.