How Globe Valves Work: A Technical Overview

Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Globe valves play a crucial role in regulating and controlling the flow of fluids within various systems. Comprised of two halves with a movable plug or disc, they are primarily used for opening, closing, or throttling flow.
There are three basic designs of globe valve bodies: Tee, Angle, and Wye, each serving specific purposes based on their structural configurations. The stem of a globe valve moves up and down to regulate flow inside the valve, containing a disc and seat, which are screwed into the valve body.
Globe valves are commonly utilized in cooling water systems, fuel oil systems, feedwater or chemical feed systems, boiler and main steam vents and drains, turbine lube oil systems, and others. They offer advantages such as good throttling and shutoff capabilities, ease of maintenance, and the versatility to be used as a stop-check valve under certain conditions.
Understanding Globe Valves
Globe valves are essential components in the fluid control system, used to regulate and stop the flow of liquids or gases. Here’s a breakdown of the components and functions of globe valves.
Definition and Basic Design
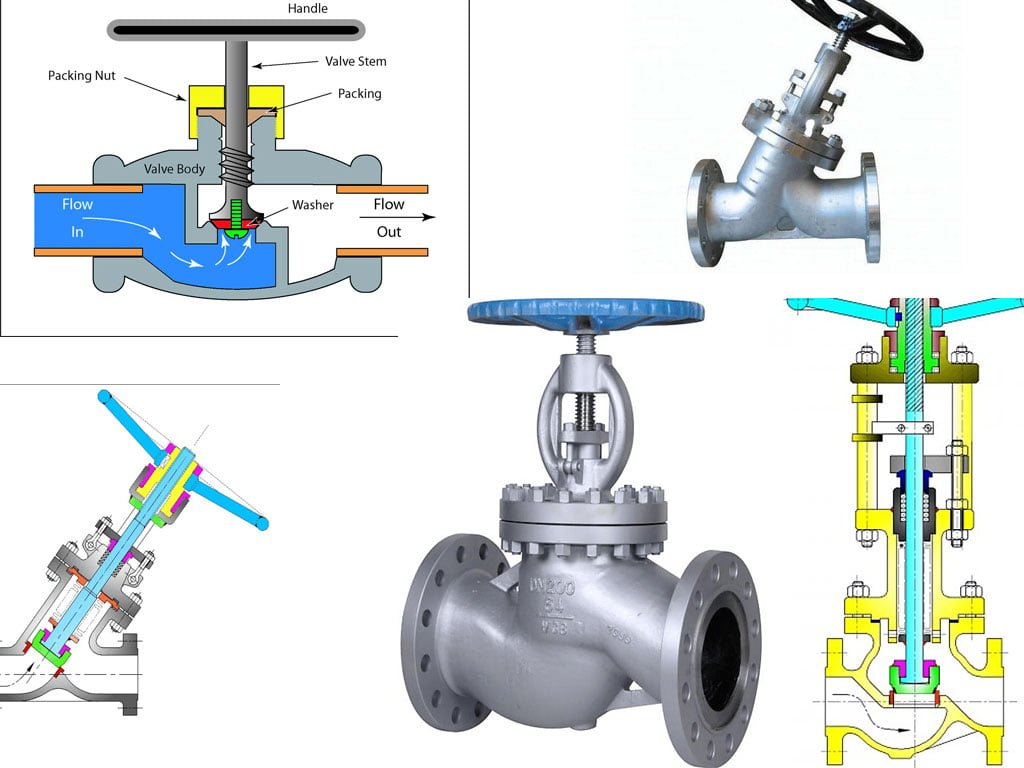
Globe valves, as the name suggests, have a globe-shaped body. These valves consist of a movable disk-type element and a stationary ring seat in a spherical body. When the valve is open, the flow is regulated by the position of the disk relative to the seat.
The Components of a Globe Valve
The main components of a typical globe valve include the valve body, bonnet, disc, stem, seat, and handwheel. The valve body is the primary pressure boundary, while the bonnet houses the stem and disk assembly. The disc moves perpendicular to the seat to stop or regulate the flow.
Types of Globe Valves
There are several variations of globe valves including angle, T-pattern, and Y-pattern globe valves. These differ in body shape, stem orientation, and the flow path, allowing for specific applications and flow control requirements.
The Function of Globe Valve Stems and Discs
The stem and disc play a crucial role in the functionality of globe valves. The stem connects the actuator to the disc, allowing for the movement of the disc to regulate the flow. The disc interacts with the seat to modulate the flow, ensuring precise control over the fluid or gas passing through the valve.

Operating Principles
A globe valve operates by regulating the flow of fluid through a mechanism that involves a movable disc and a stationary seat. As the handwheel is turned, the stem moves the disc up or down into the flow path, increasing or decreasing the flow rate.
The disc and seat play a critical role in controlling and regulating the fluid flow. The disc, when in the closed position, makes contact with the seat, completely obstructing the flow. When the valve is opened, the disc is lifted away from the seat, allowing the fluid to pass through.
The direction of flow within the globe valve is typically from the lower part of the valve to the upper part, through the seat and around the disc. This configuration ensures efficient regulation and control of the flow of fluids within the valve.
Understanding the Operating Principles of Globe Valves
Globe valves are essential components in various industrial applications due to their ability to regulate and control the flow of liquids or gases. Understanding the operating principles of globe valves is crucial for ensuring efficient and reliable operations in different systems. In this article, we will delve into the technical aspects of globe valves and explore their operating principles in detail.
1. Design and Construction
Globe valves feature a spherical body with an internal baffle and a movable plug or disc that can be adjusted to regulate the flow. The design includes an inlet and outlet port, as well as a valve stem that connects to the plug. This construction allows for precise control over the flow of fluid or gas through the valve.
2. Flow Regulation
The operating principle of a globe valve involves the movement of the plug or disc to either restrict or allow the flow of the medium. By turning the valve stem, the plug can be positioned to control the size of the flow passage, thereby regulating the flow rate. This ability to adjust the flow makes globe valves suitable for applications that require fine-tuning of fluid or gas movement.
3. Pressure and Shut-Off Capability
Globe valves are designed to withstand high-pressure environments, making them suitable for applications where pressure regulation is critical. The valve’s structure allows for a tight seal when fully closed, preventing any leakage or backflow. This shut-off capability is essential for maintaining system integrity and preventing potential hazards.
4. Versatility and Applications
Due to their versatile operating principles, globe valves are used in various industries, including oil and gas, petrochemical, pharmaceutical, and manufacturing. Their ability to handle different types of fluids and gases, along with their reliable flow control, makes them a popular choice for diverse applications.
5. Actuation Options
Globe valves can be operated manually or through automated means such as pneumatic, electric, or hydraulic actuators. This flexibility in actuation options enhances the valve’s adaptability to different operational requirements, allowing for seamless integration into complex systems.
Understanding the operating principles of globe valves is essential for engineers, technicians, and professionals working in industries where flow control is crucial. By grasping the technical aspects of these valves, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their selection, installation, and maintenance, ultimately contributing to the efficiency and safety of industrial processes.
How Globe Valves Work
Globe valves are used to control the flow of fluid in a pipeline. They are designed with a mechanism that allows for efficient regulation and throttling of the flow.
The Mechanism of Opening and Closing
Globe valves work by using a plug (disc or ball) that is connected to a stem. When the stem is turned, the plug moves up or down, allowing the valve to open or close. This mechanism provides precise control over the flow of fluid, making globe valves suitable for applications requiring accurate flow regulation.
Flow Regulation and Throttling
The design of globe valves enables them to effectively regulate the flow of fluid. By adjusting the position of the plug, the flow can be gradually increased or decreased, providing smooth and precise control. This makes globe valves ideal for situations where throttling of the flow is necessary to maintain optimal system performance.
The Role of the Valve Seat
The valve seat in a globe valve plays a crucial role in controlling the flow of fluid. It is the sealing surface between the plug and the valve body. When the valve is closed, the plug makes contact with the valve seat, preventing the flow of fluid. This tight seal ensures that there is no leakage, making globe valves an efficient choice for applications where leak prevention is essential.
Conclusion
In conclusion, globe valves function by using a moveable plug or disc to regulate the flow of fluid through a system. They are designed with a stem that moves up and down to control the flow, along with a disc and seat which are essential components. The three basic globe valve body designs – Tee, Angle, and Wye – each serve different purposes and are used in various applications based on their unique features.
Globe valves are particularly beneficial for applications where flow regulation is essential, such as cooling water systems, fuel oil systems, and feedwater or chemical feed systems. Their advantages include good throttling and shutoff capabilities, ease of maintenance, and the potential to be used as a stop-check valve.