How do Ball Valves Work: The Mechanism
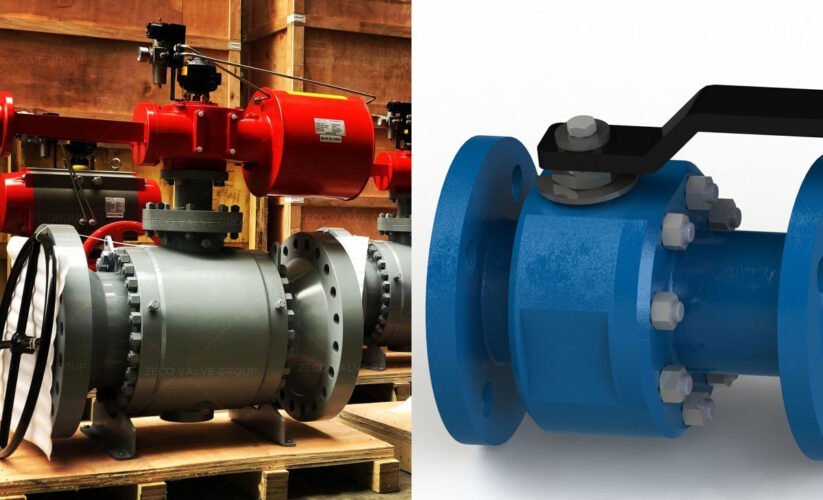
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction to Ball Valves
Ball valves are essential components in controlling the flow of liquids or gases. They utilize a rotary ball with a bore to regulate the flow by either allowing the medium to pass through or blocking it with a simple quarter turn (90 degrees) rotation. Known for their extended service life and reliable sealing, they are favored over gate valves, particularly for long-term usage. Additionally, they exhibit greater resistance to contaminated media than most other valve types. In special versions, ball valves can also serve as control valves, although this application is less common due to limited flow rate control accuracy. The sectional view in Figure 1 provides a visual representation of a ball valve’s internal structure.
Basics of Ball Valves
Ball valves are essential components in fluid pipelines, prized for their efficient regulation of flow. The valve’s design features a round ball within the valve body that administers control over the fluid flow.
Definition and Function of Ball Valves
Ball valves operate by rotating a spherical disc, commonly known as a ball, to start, regulate, or stop the flow of media. When the ball’s bore aligns with the passageway, the valve is in an open position, allowing fluid to course through the pipeline. Conversely, turning the ball 90 degrees obstructs the flow, effectively closing the valve.
The Components of a Ball Valve
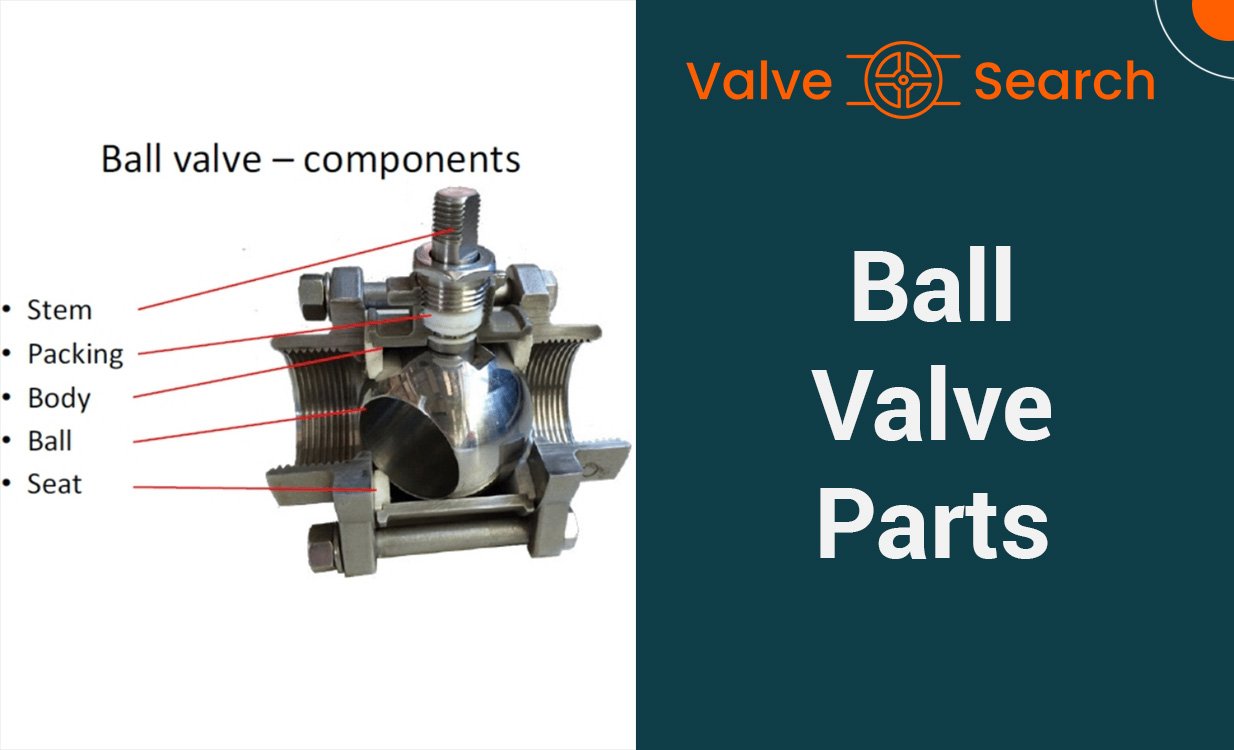
A ball valve consists of several key components, including the ball, stem, actuator, seat, body, and end connections. The ball, typically made of metal or a durable synthetic material, is pivotal in controlling the flow. The stem, connected to the ball, transmits the rotational movement. The actuator, which can be manual or automated, initiates the ball’s movement. The seat forms a tight seal with the ball, preventing fluid leakage. The body encases the internal components and provides structural support. The end connections enable the valve to join with the pipeline.
Types of Ball Valves and Their Uses
Floating Ball Valves: Floating ball valves are commonly employed in smaller and lower-pressure applications. The design encompasses a ball that floats between two seats, relying on fluid force to seal against the downstream seat. These valves are utilized in various industries, including household plumbing and chemical containment systems.
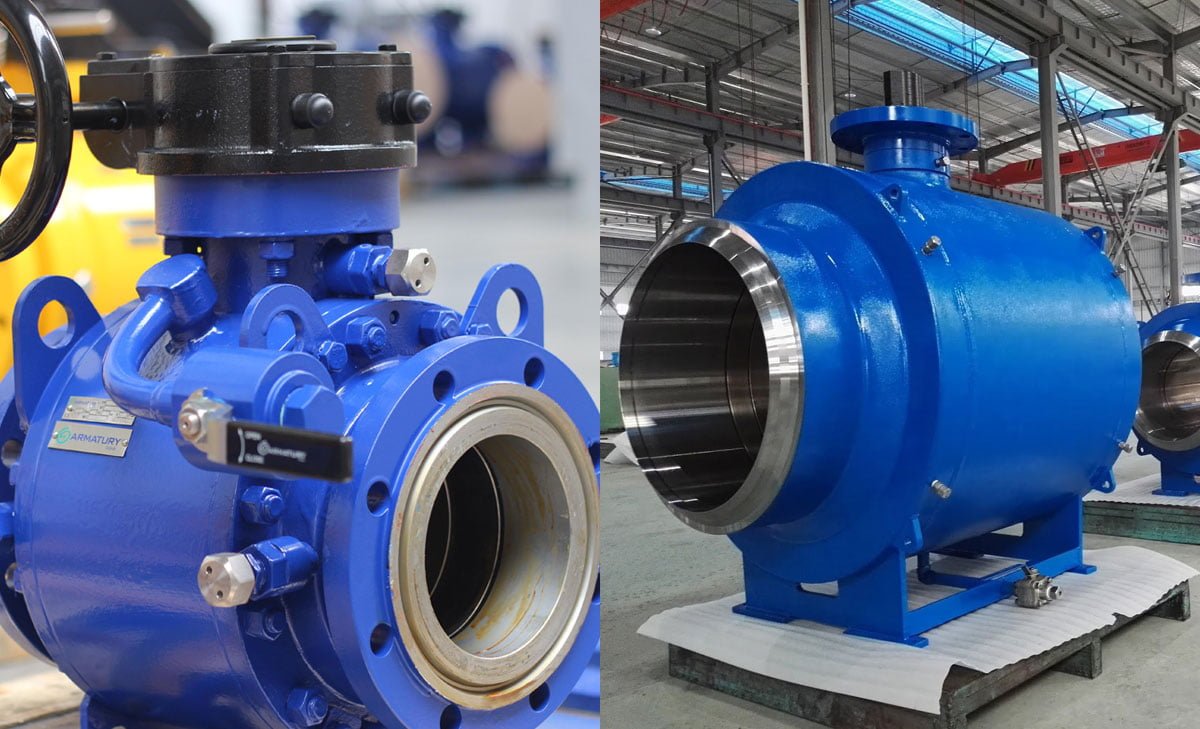
Trunnion Ball Valves: Trunnion ball valves are tailored for larger and higher-pressure applications, featuring a ball secured by trunnions, ensuring stability under extreme force. Due to their robust construction, these valves find utility in heavy-duty industrial settings, such as oil and gas production and processing facilities.
These valves are versatile and find applications in myriad industries, owing to their capability to act as on/off or control valves. The addition of partial ball and V-port ball designs enhances their suitability for precise control functions, expanding their scope of application.
How Ball Valves Operate
The Role of the Ball in Control Flow
Ball valves operate by using a spherical obstruction (the ball) to control the flow of liquids or gases. When the valve is open, the fluid or gas flows through a hollowed-out portion within the ball. When the valve is closed, the ball is rotated 90 degrees to block the flow. This simple and effective design allows for quick and precise control of the flow, making them a popular choice in various industries.
Quarter-Turn Functionality
One unique feature of ball valves is their quarter-turn operation. This means that the valve handle only needs to be turned 90 degrees to open or close the valve fully. This swift and uncomplicated mechanism is advantageous in applications where rapid flow control is necessary, enhancing efficiency and minimizing downtime.
Sealing Mechanism Explained
The sealing mechanism of ball valves is crucial in preventing leakage. When the valve is closed, the ball is pressed against the valve seat, creating a tight seal that prevents the flow of fluid or gas. This design ensures minimal leakage and provides reliable shutoff capabilities, making them suitable for both high and low-pressure applications.

Ball Valve Materials and Construction
Selecting the appropriate materials for ball valves is essential for their performance and longevity. The varying parts of a ball valve, including the housing, ball, and seal, can be constructed from different materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, brass, and PVC. Each material offers unique characteristics that make it suitable for specific applications.
Common Materials for Ball Valve Parts
The housing of a ball valve is commonly made from materials like stainless steel, brass, and PVC (polyvinyl chloride), while the ball itself is typically constructed of chrome-plated steel, chrome-plated brass, PVC, or stainless steel. The valve seats are often made of Teflon, but they can also be composed of metals or other synthetic materials. It’s crucial to consider the chemical compatibility of these materials with the intended media and operating conditions.
Durability and Resistance Factors
When assessing ball valve materials, factors such as corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and temperature tolerance must be taken into account. For instance, stainless steel offers exceptional corrosion resistance and strength, while brass is known for its durability. PVC, on the other hand, is resistant to various chemicals but has temperature limitations.
High-Pressure Ball Valves Design
In high-pressure applications, the design and material selection of ball valves need to withstand extreme conditions. Materials like stainless steel are commonly preferred for high-pressure ball valves due to their robustness and resistance to pressure-induced strain. The construction of high-pressure valves involves meticulous engineering to ensure structural integrity and reliable performance under challenging operational pressures.
Manual vs. Automatic Ball Valves
Ball valves are available in manual and automatic versions, each with its own unique operation and advantages. In this section, we will explore the differences and benefits of manual ball valve operation, electric ball valves, and pneumatic ball valves.
Manual Ball Valve Operation
Manual ball valves are operated by a handle, which is turned to open or close the valve. This simple and reliable operation makes manual ball valves suitable for various applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial settings. The manual operation provides a high level of control, allowing users to adjust the flow of liquids or gases with precision.
Electric Ball Valves
Electric ball valves are equipped with an electric actuator that automatically opens and closes the valve in response to an electrical signal. This automation eliminates the need for manual operation, making electric ball valves ideal for applications where remote or automated control is required. With the ability to integrate into control systems, electric ball valves offer enhanced efficiency and convenience.
Pneumatic Ball Valves
Pneumatic ball valves feature a pneumatic actuator that uses compressed air to operate the valve. These valves are commonly used in industrial environments where compressed air systems are already in place. The pneumatic actuation ensures quick and reliable valve operation, making pneumatic ball valves well-suited for demanding processes that require rapid response and precise control.
By understanding the differences between manual and automatic ball valves, users can make informed decisions when selecting the most suitable valve for their specific requirements. Whether it’s manual operation for hands-on control, electric automation for remote management, or pneumatic actuation for industrial applications, ball valves offer versatile solutions for fluid and gas flow control.
Ball Valves in Different Applications
Ball valves are versatile and find extensive use in various applications due to their numerous advantages. Whether it’s for shut-off applications, handling contaminated media, or precise control, ball valves have proven to be a reliable choice in different industries.
Advantages in Shut-off Applications
One of the primary advantages of ball valves is their efficient shut-off capability. These valves provide a tight seal when closed, effectively stopping the flow of fluids or gases. This makes them ideal for applications where leakage cannot be tolerated, such as in pipelines, gas distribution systems, and chemical processing plants. The straightforward operation of ball valves also ensures quick and reliable shut-off, contributing to their widespread use in critical shut-off applications.
Ball Valves for Contaminated Media
In industries dealing with contaminated or abrasive media, ball valves demonstrate exceptional resilience. Their design minimizes the risk of build-up and clogging, which can be a common issue in such environments. The smooth bore of the ball allows for easy cleaning and prevents potential blockages, making them well-suited for handling challenging media like slurries, wastewater, and corrosive chemicals.
Control Valves
For precise flow control, ball valves offer a responsive solution. With their ability to modulate flow rates accurately, they serve as effective control valves in various systems. This makes them valuable in processes that require precise regulation of fluid or gas flow, such as in HVAC systems, industrial automation, and water treatment facilities. The simplicity and reliability of ball valves make them a preferred choice in control applications where accuracy is paramount.
In summary, the adaptable nature of ball valves lends itself to a wide range of applications, from critical shut-off tasks to managing demanding media and providing accurate flow control. Their effectiveness in these diverse roles underscores their significance across numerous industrial and commercial settings.
Maintenance and Longevity of Ball Valves
Service Life Expectancy
Ball valves are known for their durability and long service life expectancy. With proper maintenance, they can last for many years without significant degradation in performance. The service life of ball valves is largely dependent on the quality of materials used in their construction and the operating conditions to which they are subjected. High-quality ball valves, when maintained properly, can have a service life spanning decades.
Reliability and Sealing Over Time
One of the key factors in determining the longevity of ball valves is their reliability and sealing over time. As ball valves are operated, the sealing surfaces may experience wear due to friction and the flow of media. Proper lubrication and periodic inspection can help prevent premature wear and ensure continued sealing reliability. The design of ball valves also contributes to their reliability, with many modern ball valves featuring advanced sealing technologies that enhance their longevity.
Tips for Maintaining Ball Valves
To maintain the longevity of ball valves, it is important to follow a regular maintenance schedule. This may include periodic inspections for leaks, proper lubrication of moving parts, and cleaning to remove any debris that could affect performance. Additionally, maintaining proper pressure and temperature conditions during operation can help extend the service life of ball valves. Regularly checking for signs of wear and addressing any issues promptly can prevent costly downtime and ensure the continued reliable operation of ball valves.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the ball valve mechanism operates by rotating a ball with a bore to control the flow of liquid or gas. This quarter turn action either allows the medium to flow through or blocks it. Ball valves are known for their long service life and reliable sealing, even when not in use for extended periods. They are more resistant to contaminated media compared to other valve types. While less common, ball valves can also be used as control valves, offering advantages such as reliable sealing even with dirty media. Overall, ball valves are a popular choice for shut-off applications due to their durability and sealing capabilities.