Pressure Reducing Valves: Guardian of Water Pressure

Are you having trouble maintaining optimal water pressure in your plumbing system? A pressure reducing valve, commonly referred to as a PRV, could be the solution you need. Whether for residential or commercial applications, maintaining the right water pressure is crucial for the proper functioning of your plumbing system. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the significance of pressure reducing valves, how they operate, and why they’re essential for your plumbing system’s health.
A pressure reducing valve is a crucial component of any plumbing system, as it helps ensure that the water pressure remains at an optimal level. Without this valve, high water pressure could lead to leaks, pipe damage, or even appliance malfunctions. By understanding the role of reducing pressure valves and how they function, you can effectively maintain the integrity of your plumbing system. So, let’s dive in and explore everything you need to know about PRVs.

Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Pressure Reducing Valves
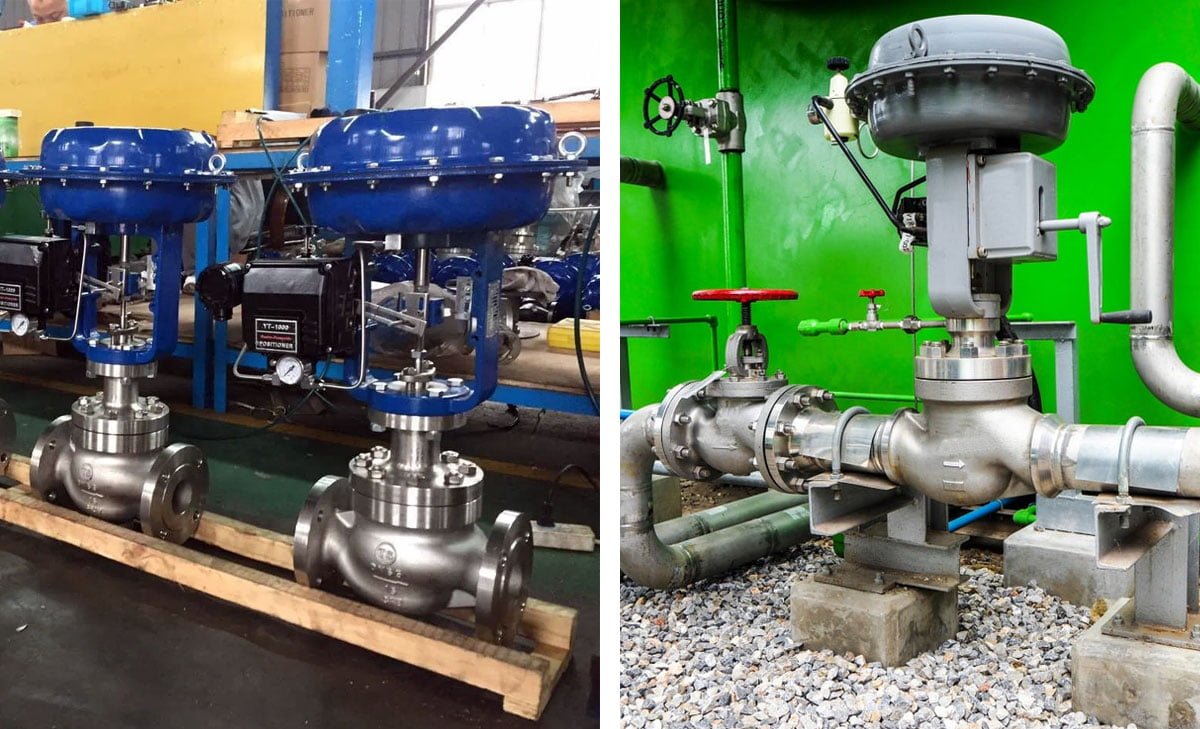
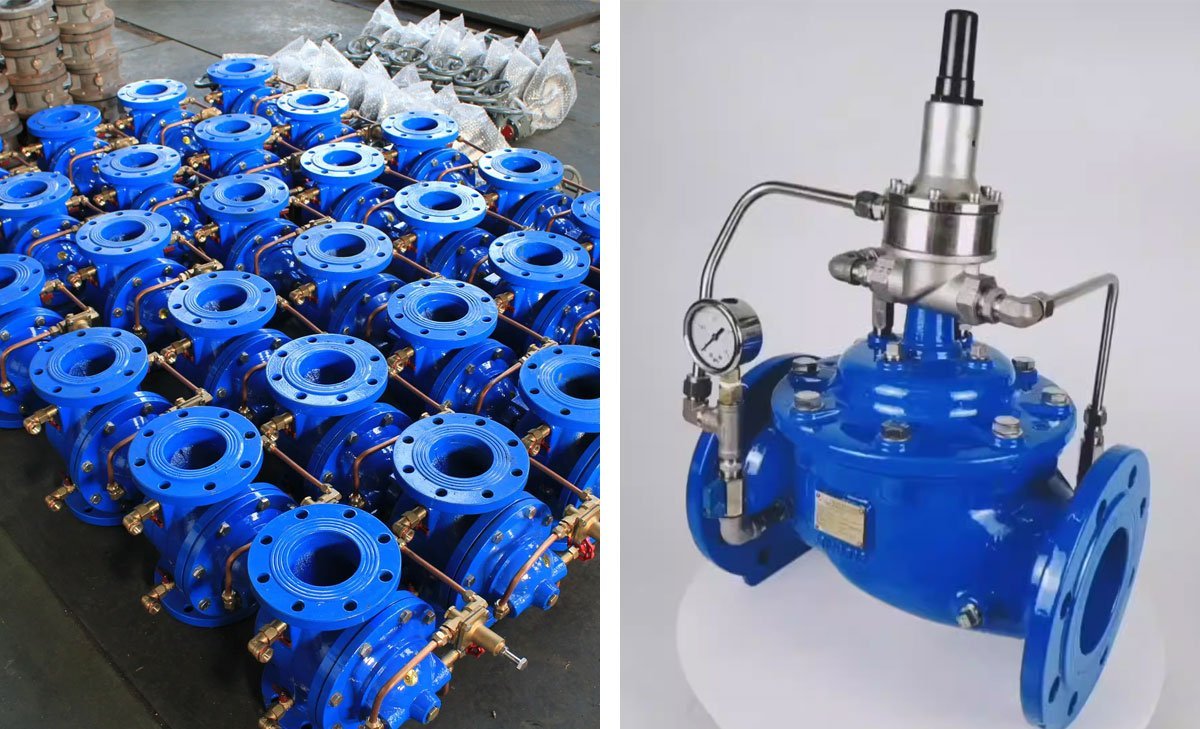
A pressure reducing valve (PRV) is a vital component of plumbing and water systems, designed to regulate the flow and pressure of water within a building. It is commonly installed where the municipal water supply enters a residential or commercial property.
What is a Pressure Reducing Valve?
A pressure reducing valve, also known as a water pressure regulator, is a mechanical plumbing device that reduces and stabilizes the incoming water pressure from the main water supply. This ensures that the water pressure reaching the internal plumbing system remains at a safe and consistent level.
Importance of Water Pressure Regulation
Maintaining the optimal water pressure within a plumbing system is crucial to prevent potential issues such as leaks, pipe bursts, or damage to appliances. Unregulated high water pressure can put stress on pipes, leading to premature deterioration and an increased risk of leaks.
Conversely, low water pressure can result in reduced performance of fixtures such as showers, faucets, and appliances like dishwashers and washing machines. Pressure reducing valves play a critical role in addressing these concerns by providing a steady and controlled flow of water throughout the plumbing system.
Regulating water pressure also contributes to water conservation by preventing excessive water usage and reducing the strain on the overall plumbing infrastructure.
In summary, pressure reducing valves are essential for maintaining the integrity of plumbing systems and ensuring the efficient operation of household and commercial appliances by effectively managing water pressure.
By strategically implementing pressure reducing valves, property owners can significantly prolong the lifespan of their plumbing infrastructure, minimize water wastage, and enhance the overall functionality of their water supply systems.
Functionality of Pressure Reducing Valves
Pressure reducing valves (PRVs) play a crucial role in maintaining optimal water pressure in various applications. Understanding the functionality of PRVs involves delving into their mechanism of operation and the key components responsible for regulating pressure.
Mechanism of Operation
PRVs operate based on the principle of controlling the downstream pressure to a set level, regardless of fluctuating upstream pressure. The inner workings of a pressure reducing valve center around the interaction of diaphragms, springs, and adjustments to sustain the desired pressure levels.
When the upstream pressure exceeds the set level, the diaphragm within the valve responds to the excess force by slightly shifting, causing the valve to constrict the flow of water. Conversely, if the upstream pressure falls below the set level, the spring-loaded diaphragm allows the valve to open, ensuring a consistent downstream pressure.
The intricate balance between the diaphragm and the spring enables the valve to modulate the water flow, maintaining a stable pressure output to the connected system or appliances.
Components and Their Functions
- Diaphragm: The diaphragm serves as the responsive element within the pressure reducing valve. When subjected to varying pressures, it flexes to modulate the valve’s opening and closing, thereby regulating the flow of water.
- Spring: Central to the functionality of the PRV, the spring provides the necessary counterforce to the diaphragm. It ensures that the valve responds appropriately to fluctuations in upstream pressure, contributing to the precise control of downstream pressure.
- Adjustment Mechanism: Many pressure reducing valves feature adjustable settings to customize the desired downstream pressure. This mechanism allows for fine-tuning the valve in accordance with specific system requirements, ensuring optimal performance.
- Valve Body: The physical structure of the valve body plays a critical role in directing the flow of water and housing the diaphragm and spring components. The design and materials of the valve body influence its durability and ability to withstand varying pressures.
By comprehensively understanding the inner workings and components of pressure reducing valves, users can effectively leverage this essential device to maintain consistent water pressure in diverse applications.

The Technical Functions of a Pressure Reducing Valve
Pressure reducing valves (PRVs), also known as water pressure reducers or water pressure regulators, are essential components in plumbing systems. They serve the crucial function of maintaining optimal water pressure within a specified range, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of various plumbing fixtures and appliances. Here are the technical functions of a PRV:
Pressure Regulation: The primary function of a pressure reducing valve is to regulate and reduce the incoming water pressure from the main supply line to a safe and consistent level for distribution within a building or a specific area. This helps prevent damage to pipes, fixtures, and appliances that could result from excessively high water pressure.
Flow Control: Water PRVs are designed to control the flow of water by automatically adjusting the valve opening based on the varying inlet pressure. This ensures a steady flow of water at the desired pressure, regardless of fluctuations in the supply line pressure.
Pressure Monitoring: Modern pressure reducing valves are equipped with built-in pressure monitoring mechanisms that enable them to sense changes in the inlet pressure. Once the preset pressure level is reached, the valve modulates to maintain a constant outlet pressure, effectively safeguarding the plumbing system.
Pressure Relief: In the event of a sudden surge in water pressure, which could occur due to factors such as water hammer or the opening and closing of other water outlets, the pressure reducing valve acts as a protective barrier (relief valve) by relieving the excess pressure and preventing potential damage to the system.
System Protection: By maintaining consistent and controlled water pressure, PRVs play a critical role in protecting water heaters, dishwashers, washing machines, and other appliances that are sensitive to high water pressure. This helps extend the lifespan of such equipment and reduces the risk of costly repairs.
Noise Reduction: Another notable function of pressure reducing valves is their ability to minimize water hammer and pipe resonance, which can cause disruptive and potentially damaging noises in plumbing systems. The valve’s controlled pressure reduction contributes to a quieter and more stable water distribution system.
In conclusion, understanding the technical functions of a pressure reducing valve is essential for ensuring the reliability and longevity of plumbing systems. From pressure regulation and flow control to pressure monitoring and system protection, PRVs play a vital role in maintaining optimal water pressure and safeguarding the entire plumbing infrastructure.
Remember to consider the specific requirements of your plumbing system and consult with a professional for the proper selection, installation, and maintenance of PRVs to maximize their effectiveness and longevity.
Applications and Installation
Pressure reducing valves (PRVs) are essential components in plumbing systems, ensuring the appropriate delivery of water to various types of properties. From residential homes to large-scale commercial and industrial facilities, PRVs play a crucial role in maintaining safe and efficient water pressure levels. This section will delve into the specific applications of PRVs and provide valuable insights into their installation across different settings.
Residential Use
In residential plumbing systems, PRVs are tasked with reducing the incoming high pressure of water into a lower and safer pressure for homes. This is vital for protecting household appliances, fixtures, and pipelines from potential damage caused by excessive water pressure.
Specific Applications
- Household Appliances: PRVs are commonly installed to safeguard water heaters, washing machines, dishwashers, and other appliances that require regulated water pressure for optimal performance and longevity.
- Fixture Protection: By controlling water pressure, PRVs help prevent leaks, bursts, and premature wear in faucets, toilets, and showerheads, prolonging the lifespan of these fixtures.
Common Installation Points and Maintenance Tips
- Main Water Line: Pressure reducing valves are typically installed near the main water entry point of a residence, often before the water meter. This strategic placement ensures comprehensive pressure management for the entire property.
- Maintenance: Homeowners should schedule periodic inspections of their PRVs to check for potential leaks, corrosion, or erratic pressure fluctuations. Regular maintenance will ensure that the PRV continues to function effectively in protecting the plumbing system.
Commercial & Industrial Applications
In commercial and industrial settings, the applications of pressure reducing valves expand to accommodate larger water distribution networks and specialized operational requirements. The scale and complexity of installations in these environments demand robust and precision-engineered PRVs to fulfill diverse needs.
Broader Uses
- Institutional Facilities: PRVs are integral in maintaining consistent water pressure for schools, hospitals, government buildings, and other institutional structures, catering to high-demand water usage while upholding safety standards.
- Industrial Complexes: Manufacturing plants, refineries, and production facilities rely on PRVs to regulate water pressure for various processes, including cooling, heating, and general utility services.
Scale and Complexity of Installations
- Customized Solutions: Due to the unique demands of commercial and industrial operations, PRVs in these environments are often customized to manage high-flow rates and accommodate specific pressure settings.
- Regular Monitoring: Given the critical role of PRVs in sustaining industrial processes, proactive monitoring and maintenance routines are crucial to ensure continuous, uninterrupted performance.
By understanding the diverse applications and installation requirements of pressure reducing valves in residential, commercial, and industrial contexts, property owners and facility managers can optimize water pressure management to enhance overall system efficiency and longevity.

Selecting the Right Pressure Reducing Valve
When choosing a pressure reducing valve (PRV), certain factors need to be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with specific systems.
Factors to Consider
Key considerations when selecting a pressure reducing valve include the following:
- Flow Rate: The flow rate of the system is a critical factor in determining the appropriate pressure reducing valve. It is essential to match the flow capacity of the valve with the anticipated flow rate to maintain consistent pressure regulation.
- Material: Consider the material of the valve based on the application and the type of fluid being regulated. Ensure that the material is suitable for the specific environmental conditions and fluid properties to avoid corrosion or degradation.
- System Compatibility: Compatibility with existing plumbing systems, equipment, and fittings is crucial. The pressure reducing valve should seamlessly integrate into the system without causing any disruptions or inefficiencies.
Sizing and Schematic Design
Proper sizing and schematic design are fundamental aspects of ensuring the effective functionality of pressure reducing valves within plumbing networks.
- Sizing Considerations: The size of the PRV should be compatible with the existing pipe size and flow demand. It is essential to accurately calculate the required pressure drop to determine the appropriate sizing of the valve. Utilizing sizing calculators or consulting with industry resources can aid in determining the correct valve size for the specific application.
- Schematic Design Layout: The design layout of the plumbing network plays a significant role in the performance of pressure reducing valves. The location, orientation, and installation of the valve within the system should be carefully planned to minimize pressure fluctuations and ensure consistent pressure regulation throughout the network.
By carefully evaluating these factors and considerations, it becomes feasible to select the right pressure reducing valve that aligns with the unique requirements of the plumbing system, ensuring reliable and efficient pressure regulation.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Pressure reducing valves require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. By implementing routine maintenance practices and proactively addressing common issues, you can enhance the efficiency and reliability of your PRV system.
Routine Maintenance Practices
To maintain the functionality of pressure reducing valves, several regular maintenance tasks should be performed. These practices not only prolong the lifespan of the valves but also contribute to the overall smooth operation of the system.
- Inspection and Cleaning: Regularly inspect the pressure reducing valve for any signs of leaks, cracks, or damage. Additionally, clean the valve and its components to prevent the accumulation of debris, sediment, or mineral deposits that could impede its functionality.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication of the moving parts is vital for the smooth operation of pressure reducing valves. Apply manufacturer-recommended lubricants at specified intervals to ensure the components function optimally.
- Pressure Adjustment: Periodically check the upstream pressure and adjust it if required to maintain the recommended pressure levels. This step is crucial for sustaining the valve’s ability to regulate pressure effectively.
- Component Replacement: Stay vigilant for any signs of wear or malfunctioning parts within the PRV. Replace cartridges or components as necessary to prevent potential system failures.
Common Issues and Solutions
Despite regular maintenance, pressure reducing valves may encounter common issues that require prompt attention. Identifying these issues and having a clear understanding of troubleshooting steps and potential remedies is essential for maintaining system efficiency.
- Leakage and Cracks: Any leaks or cracks in the pressure reducing valve can significantly impact its effectiveness. Regularly inspect the valve for leaks or cracks, and promptly address them to prevent further damage and loss of pressure regulation.
- Pressure Fluctuations: Sudden fluctuations in pressure levels can indicate a problem with the valve. Troubleshoot the system to identify the root cause of pressure irregularities and take corrective action to restore stable pressure regulation.
- Inadequate Performance: If the pressure reducing valve fails to maintain consistent pressure levels, it could be due to internal blockages or component malfunctions. Thoroughly inspect the valve and its components, and implement the necessary repairs or replacements to restore its optimal performance.
- Pilot System Issues: The pilot system of the PRV requires pressurized water to function properly. Any disruptions or malfunctions in the pilot system can affect the overall pressure regulation. Troubleshoot the pilot system and address any issues to ensure its seamless operation.
By adhering to a comprehensive maintenance routine and promptly addressing common issues with pressure reducing valves, you can uphold the reliability and efficiency of your system, ultimately maximizing its operational longevity and performance.
For further insights into maintaining and troubleshooting pressure reducing valves, consult industry resources and manufacturer guidelines to ensure the best practices are employed.
Best Practices for Optimal Performance
Water quality plays a significant role in the proper functioning and longevity of a water PRV. Poor water quality can lead to corrosion and sediment buildup, impacting the effectiveness of the valves. To mitigate these issues, it is essential to implement the following best practices:
Water Quality Considerations
Water containing high levels of minerals, such as calcium and magnesium, can lead to mineral deposits within the valve, affecting its performance over time. To address this, regular water testing and the implementation of water softening systems can help maintain optimal water quality. In addition, installing a strainer upstream of the pressure reducing valve can help prevent debris and sediment from entering and causing damage.
Integration with Smart Plumbing Systems
Pressure reducing valves are compatible with modern smart plumbing technologies, offering enhanced control and efficiency within plumbing systems. By integrating PRVs with smart water monitoring systems, users can remotely monitor and adjust water pressure, ensuring optimal performance and reducing unnecessary strain on the valves. Additionally, the integration with smart leak detection systems can provide real-time alerts in the event of any pressure irregularities, allowing for prompt maintenance and preventing potential valve damage.
Incorporating these best practices ensures the optimal performance and longevity of pressure reducing valves within plumbing systems, ultimately contributing to efficient water usage and reduced maintenance costs.
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only and does not serve as professional advice. It is recommended to consult a qualified plumber or specialist for specific plumbing system concerns.
Hot Water Pressure Reducing Valve Usage
Hot water pressure reducing valves are essential components in plumbing systems, particularly in hot water heaters and boilers. Understanding their usage and benefits is crucial for maintaining optimal water pressure and preventing potential damage to the system. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the key aspects of using pressure reducing valves for hot water systems.
Understanding the Function of Pressure Reducing Valves
Pressure reducing valves for hot water systems are designed to automatically reduce and stabilize the pressure of the incoming water supply. This is critical for protecting the plumbing infrastructure, water heaters, and boilers from excessive pressure, which can lead to leaks, bursts, or other damage.
Installation Considerations for Hot Water Heaters
When installing a pressure reducing valve for a hot water heater, it’s important to position it correctly in the plumbing system. The valve should be placed after the main shut-off valve and before any branch lines to ensure that the entire hot water supply benefits from the regulated pressure.
Benefits of Using Pressure Reducing Valves for Hot Water Systems
Implementing a pressure reducing valve in a hot water system offers several advantages. It helps to extend the lifespan of water heaters and boilers by reducing the stress caused by high water pressure. Additionally, it contributes to energy efficiency and water conservation by optimizing the flow and pressure.
Maintenance and Monitoring of Pressure Reducing Valves
Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the proper functioning of pressure reducing valves. Monitoring for signs of leaks, corrosion, or pressure fluctuations is essential for early detection of potential issues. Additionally, periodic testing of the valve’s performance can help prevent unexpected failures.
Choosing the Right Pressure Reducing Valve for Boilers
When selecting a pressure reducing valve for a boiler, factors such as the maximum inlet pressure, flow capacity, and temperature ratings must be carefully considered. It’s essential to choose a valve that is specifically designed for the demanding conditions of boiler systems to ensure reliable and safe operation.
Regulatory Compliance and Codes
Compliance with plumbing codes and regulations is paramount when installing pressure reducing valves for hot water systems. Understanding the specific requirements and standards set forth by local authorities and industry guidelines is essential to ensure that the installation and operation of the valve are in full compliance.
In conclusion, the usage of PRVs in hot water systems, whether for heaters or boilers, is a critical aspect of maintaining efficient and safe plumbing infrastructure. By understanding their function, installation considerations, benefits, maintenance requirements, and regulatory aspects, plumbing professionals and homeowners can ensure the proper utilization of these essential components. Implementing and maintaining pressure reducing valves not only protects the system from damage but also contributes to the overall reliability and longevity of hot water systems.
Conclusion
Now that we’ve delved into the intricate workings of pressure reducing valves and explored the various factors to consider when selecting and installing one, it’s clear that these devices play a crucial role in maintaining safe and efficient water pressure in plumbing systems. From understanding the principles behind their operation to grasping the significance of proper maintenance, we’ve covered a comprehensive array of information related to water PRVs.
In the next sections, we will explore real-life scenarios where these valves can make a significant difference and how to troubleshoot common issues that may arise, ensuring that you have all the necessary knowledge to make the most of pressure reducing valves in your plumbing systems.