The Importance of Foot Valves in Pump Systems: Function and Role in Preventing Backflow

Table of Contents
ToggleIn-Depth Guide: The Role of Foot Valves in Keeping Pump Systems Efficient
The importance of foot valves in pump systems cannot be overstated. These crucial components play a vital role in preventing backflow and maintaining the efficiency of the entire system. Understanding their function is essential for ensuring the smooth operation of pump systems and preventing potential issues that could arise from backflow. In this blog post, we will delve into the function and role of foot valves, shedding light on their significance in maintaining the integrity of pump systems.
Brief
Function of Foot Valves in Pump Systems
- Foot valves are one-way check valves installed at the inlet of a pump to maintain prime and prevent backflow.
- They allow fluid to enter the pump while preventing it from flowing back out when the pump is not in operation.
Role in Preventing Backflow
- Foot valves play a crucial role in preventing backflow by ensuring that the pump remains primed and ready for operation.
- This helps to maintain consistent pressure and flow within the system, preventing damage and inefficiencies caused by reverse flow.
Importance in Pump Systems
- Without a foot valve, a pump can lose prime, leading to increased wear and tear on the pumping system and potential damage to the pump itself.
- Foot valves also help to protect the integrity of the entire system by preventing the introduction of air or contaminants from backflow.
Conclusion
- In summary, foot valves are integral components of pump systems, serving to maintain prime, prevent backflow, and safeguard the efficiency and longevity of the entire pumping system.
Exploring Pump Systems and Their Components
The Basic Mechanics of Pump Systems
Pump systems are the workhorses of various industries, responsible for the efficient transfer of liquids from one place to another. The basic mechanics of a pump system involve the conversion of mechanical energy, typically from a motor, into hydraulic energy to move fluid through a piping system. This conversion is achieved through the action of impellers or pistons, which create a flow and pressure within the system.
Critical Components
Within the intricate setup of a pump system, there are several critical components that work in unison to ensure the smooth functioning of the entire system. These components include the pump housing, impeller, motor, inlet and outlet ports, and the foot valve. The pump housing serves as the enclosure for the impeller and provides structural support to the system. The impeller, on the other hand, is responsible for generating the flow and pressure necessary to propel the fluid. The motor provides the mechanical energy required for the operation of the pump, while the inlet and outlet ports facilitate the intake and discharge of the liquid.
Overall, understanding the basic mechanics and critical components of pump systems is essential to grasp the significance of individual elements, such as foot valves, in ensuring the efficiency and longevity of the system.
The Role of Foot Valves in Pump Systems
Ever wondered how water stays in your pipes after a pump is turned off? Once a pump is turned off, doesn’t gravity just drain the water out of the pipes? Keep reading to find out how foot valves can help, plus how they can stop your pumps from being damaged.
What Is a Foot Valve?
A foot valve is a type of check valve specifically designed to be installed at the end of a pump’s suction line. It is a spring-loaded valve that allows water to flow when the pump is running but prevents backflow when the pump is turned off. Additionally, foot valves are equipped with a strainer to prevent debris from obstructing the valve’s function.
How Foot Valves Differ from Check Valves
Foot valves are a type of check valve, but they are uniquely tailored to the end of a pump’s suction line. This specialized design enables foot valves to effectively manage water flow in pump systems, preventing backflow and maintaining prime in the pump.
The Mechanism of Foot Valves
The mechanism of a foot valve involves a spring-loaded design that facilitates the opening and closing of the valve. This functionality allows water to be drawn into the pump when the system is operational and prevents the water from flowing back when the system is inactive. Additionally, the strainer attached to the foot valve plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of the valve by preventing debris from impeding its functionality.
Do you ever wonder why water doesn’t flow back out of the suction line when the pump is turned off? The answer lies in the functionality of these valves, which help maintain the prime in the pump and prevent damage. It’s like having a protective barrier at the end of the suction line, ensuring that water stays where it needs to be.

Advantages of Foot Valves in Pump&Piping Systems
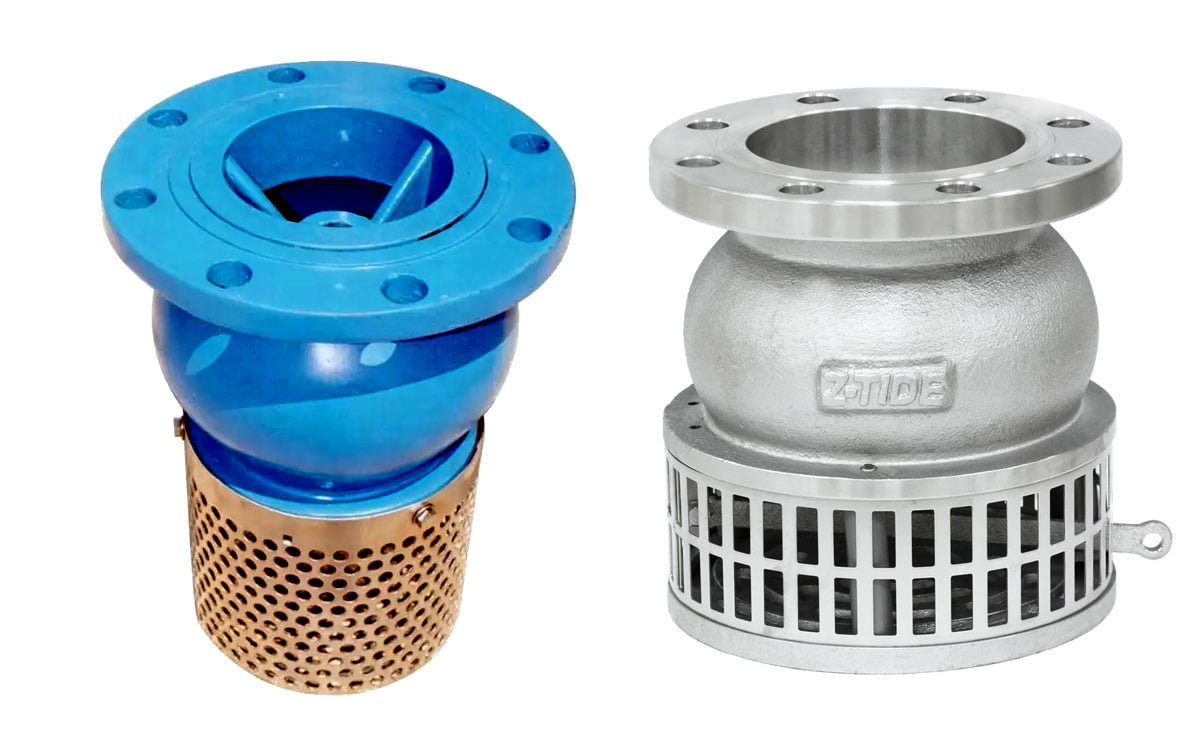
Foot valves are crucial components in pump systems, serving the vital function of preventing backflow and maintaining prime. Understanding the role and importance of foot valves is essential for ensuring the efficient and effective operation of pump systems. In this listicle, we will delve into the key functions and significance of foot valves in pump systems, shedding light on their role in preventing backflow and maintaining optimal performance.
Benefits of Foot Valves
Preventing Backflow
Foot valves play a critical role in preventing backflow in pump systems. When the pump is turned off, the foot valve ensures that the pumped fluid does not flow back into the well or water source. This helps maintain the prime and prevents the need for re-priming the pump, ultimately contributing to the overall efficiency and longevity of the system.
Maintaining Prime
One of the primary functions of foot valves is to maintain the prime in pump systems. By retaining the prime, foot valves enable the pump to start and operate effectively without the need for repeated priming. This is particularly important in applications where continuous and reliable operation is essential.
Preventing Pump Damage
Foot valves also serve to protect the pump from potential damage caused by backflow. Without a foot valve, backflow can create hydraulic shock, leading to damage to the pump impeller and other internal components. By preventing backflow, these valves help safeguard the pump and extend its lifespan.
Easing Start-Up
Foot valves contribute to the ease of start-up for pump systems. By maintaining prime and preventing backflow, foot valves ensure that the pump can start smoothly and operate efficiently without encountering issues related to airlocks or loss of prime.
Enhancing System Efficiency
Incorporating foot valves into pump systems enhances overall efficiency. By preventing backflow and maintaining prime, these valves help minimize downtime, reduce the need for manual intervention, and optimize the performance of the entire system, ultimately leading to cost savings and improved productivity.
Compatibility with Various Fluids
Foot valves are designed to be compatible with a wide range of fluids, making them versatile components suitable for diverse applications. Whether pumping water, chemicals, or other liquids, foot valves offer reliable backflow prevention and prime retention across different fluid types.
Durable and Low-Maintenance
Due to their simple yet robust design, foot valves are known for their durability and low-maintenance requirements. This characteristic makes them a cost-effective solution for long-term use in pump systems, adding value in terms of reliability and operational longevity.
In conclusion, foot valves play a crucial role in pump systems by preventing backflow and maintaining prime. Their significance in safeguarding the pump, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring smooth operation cannot be overstated. Understanding the functions and importance of these valves is essential for anyone involved in the design, installation, or maintenance of pump systems, as they are fundamental to the overall performance and longevity of the system.
Preventing Backflow: The Importance of Foot Valves
The Consequences of Backflow in Pump Systems
Backflow in pump systems can lead to a host of issues, including contamination of the water supply, which poses serious health risks. Additionally, backflow can cause damage to the pump and other system components, resulting in costly repairs and downtime. Understanding the consequences of backflow underscores the critical role foot valves play in maintaining the integrity of the system.
How Foot Valves Prevent Contamination
Foot valves act as a crucial line of defense against backflow, preventing the reverse flow of water and any contaminants it may carry. By featuring a one-way check valve, foot valves effectively ensure that water only flows in one direction, safeguarding the system from potential contamination. This vital function makes foot valves indispensable in upholding the safety and purity of the water supply within pump systems.
The Impact of Foot Valves on Water Conservation
In addition to preventing backflow and contamination, foot valves play a pivotal role in water conservation within pump systems. By maintaining prime and preventing the pump from losing its prime when not in operation, foot valves contribute to the efficient use of water. This not only conserves water resources, but also reduces energy consumption by optimizing the performance of the pump system, emphasizing the broader significance of foot valves in promoting sustainability and resource efficiency.
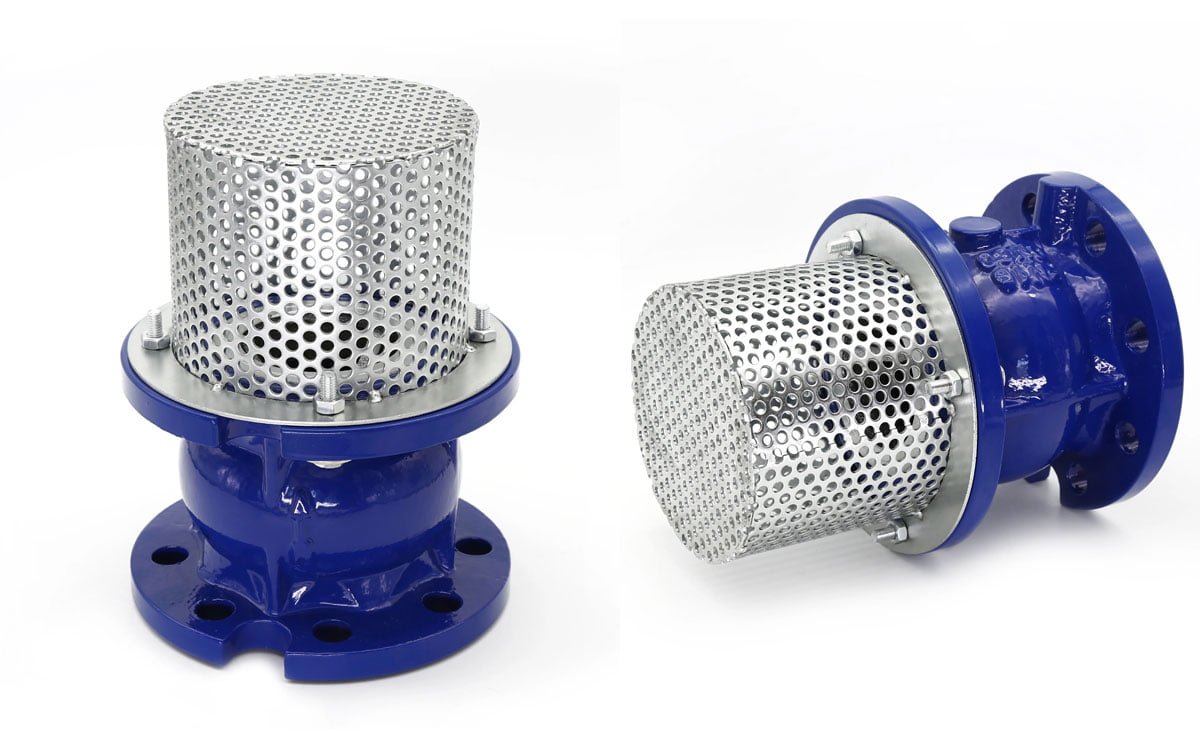

Foot Valve Installation and Maintenance
Proper Placement of Foot Valves in Pump Systems
When installing a foot valve in a pump system, it is crucial to place it at the lowest point in the suction line to ensure it is submerged in the liquid being pumped. This placement allows the valve to function effectively by preventing the pump from losing its prime. It also helps in avoiding air or vapor from entering the pump, which could lead to issues such as cavitation. Proper placement of the foot valve contributes to the overall efficiency and longevity of the pump system.
Materials and Design Considerations for Foot Valves
When selecting a foot valve, it is essential to consider the materials and design that best suit the specific application and environment. Foot valves are available in various materials such as PVC, stainless steel, and brass, each offering different levels of corrosion resistance and durability. Additionally, considering the design aspects such as flow capacity and pressure ratings is crucial in ensuring the foot valve aligns with the requirements of the pump system. Selecting the appropriate materials and design for the foot valve is vital for optimal performance and reliability.
Maintenance Tips for Foot Valve Longevity
To prolong the life of a foot valve and maintain the efficiency of the pump system, regular maintenance is imperative. Inspecting the foot valve for any signs of wear, corrosion, or debris accumulation is essential. Cleaning the valve and removing any obstructions or build-up ensures smooth operation. Additionally, greasing or lubricating moving parts as recommended by the manufacturer helps in preventing friction-related issues. Implementing a maintenance schedule and adhering to it prolongs the longevity of the foot valve, contributing to the overall operational efficiency of the pump system.
Common Applications of Foot Valves
Foot Valves in Water Distribution Systems
In water distribution systems, foot valves play a crucial role in maintaining prime and preventing backflow in pumps that draw water from wells, rivers, or lakes. These valves are installed at the foot of the suction pipe, allowing water to flow in the upward direction when the pump is activated. By maintaining the prime in the system, foot valves ensure that the pump does not run dry, thus extending its longevity and preventing damage. Additionally, they prevent water from flowing back into its source, ensuring a steady and continuous flow of water within the distribution system.
Industrial Uses of Foot Valves
In industrial settings, foot valves are essential components of pumping systems used for various applications such as irrigation, dewatering, and wastewater management. These valves are employed in industrial pumps to prevent the reverse flow of water, which could lead to pump cavitation or damage. By maintaining the hydraulic balance and preventing the loss of prime, foot valves contribute to the efficient and uninterrupted operation of industrial pumping systems, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Foot Valves in Residential Water Systems
In residential water systems, foot valves are commonly used in well pumps and irrigation systems to maintain prime and prevent backflow. By preventing water from flowing back into the well or water source, foot valves ensure the constant availability of water for domestic use and irrigation purposes. Whether it’s a shallow well pump or a residential irrigation system, the installation of foot valves is essential to maintain hydraulic efficiency, prevent pump damage, and ensure a steady flow of water for household and outdoor use.
Choosing the Right Foot Valve
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Foot Valve
When choosing a foot valve for your pump system, several factors need to be taken into consideration. The type of fluid being pumped, the operating conditions, and the specific pump requirements are crucial factors to consider in the selection process. It’s essential to ensure that the foot valve is compatible with the specific requirements of the pump system and the conditions in which it will operate.
Foot Valve Size and Flow Rate Requirements
Selecting the right size of foot valve is critical to ensure optimal system performance. The size of the foot valve should be compatible with the pump’s flow rate requirements. It’s important to match the flow rate capacity of the foot valve with the pump’s output to prevent any restrictions in the flow and maintain efficient operation. Additionally, considering the size of the inlet and outlet connections is essential to ensure seamless integration with the existing piping system.
Compatibility with Different Types of Fluids
Another crucial aspect to consider is the compatibility of the foot valve with different types of fluids. Depending on the application, the foot valve should be constructed from materials that are resistant to corrosion and erosion caused by the specific fluid being pumped. Whether it’s water, chemicals, or abrasive substances, ensuring that the foot valve is compatible with the fluid will enhance its longevity and effectiveness in preventing backflow.
By carefully considering these factors, you can confidently choose the right foot valve that aligns with the requirements of your pump system, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
FAQ: Foot Valves in Pump Systems
What is a foot valve in a pump?
A foot valve is a type of check valve located at the lower end of the suction pipe of a pump. It allows liquid to enter the pump while preventing it from flowing back out.
What is the function of the foot control valve?
The foot-operated valve is a means of applying air to operate the brakes. The amount of distance the treadle of the foot valve is depressed by the driver determines the amount of air pressure that will be applied, but the maximum application will not exceed the pressure in the reservoir.
Can a water pump run without a foot valve?
When the pump is shut off, the suction disappears, and gravity affects the water column. If there wasn’t a foot valve in place, the water would flow downward through the pipe, back to its original source. The pipe would be left empty of water, instead filled with air.
What is the problem with the foot valve on a water pump?
Foot valves have three common issues: wire drawing, disc flutter, and sediment buildup in the screen. The first two issues require foot valve repair, but the third is fixable without pulling up the piping.
Conclusion
Understanding the crucial role of foot valves in preventing backflow in pump systems is essential for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of the entire system. By effectively controlling the flow of fluids and preventing reverse flow, foot valves play a pivotal role in ensuring the smooth operation of pump systems. Proper installation, maintenance, and selection of foot valves are imperative to minimize the risk of backflow and optimize the performance of pump systems.