Gate Valve vs. Ball Valve: A Comprehensive Comparison
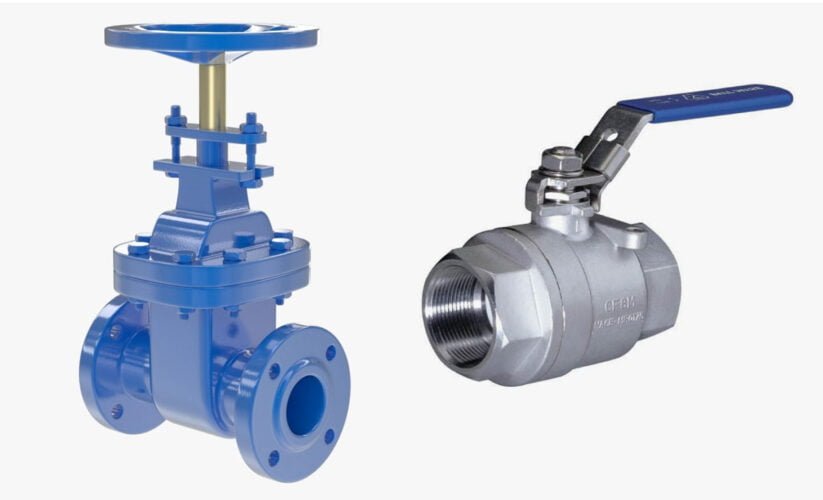

Table of Contents
ToggleGate Valve vs. Ball Valve: A Comprehensive Comparison
When considering the best valve for your application, understanding the differences between gate valves and ball valves is crucial. A gate valve employs a solid rectangular gate to control the flow of fluid, while a ball valve uses a pivoting ball with a bore to manage liquid or gas flow. The distinct structural and operational disparities between these two valve types make it essential to choose the right one for your specific needs.
Gate valves are utilized for complete fluid flow cessation or initiation by raising or lowering a solid gate. These valves do not regulate flow and are designed to be fully open or fully closed. They typically require more than a 360° turn to change the gate’s position, making them slower than ball valves. On the other hand, ball valves only necessitate a 90° turn for operation, allowing for faster on/off control. These differences in operation make each valve type suitable for specific applications.
Understanding Gate Valves
Gate valves are essential components in many fluid control systems, characterized by their simple yet effective design. Understanding the basic structure, mechanics of operation, advantages, and limitations of gate valves is crucial for making informed decisions about their use in various applications.
Basic Structure of a Gate Valve
A gate valve consists of several key parts, including the handwheel, stem, gasket, bonnet, valve body, flange, and gate. These components work together to control the flow of fluid in a pipeline. The most common connection types for gate valves are flanged and threaded, allowing for easy installation and maintenance.
The Mechanics of Gate Valve Operation
The operation of a gate valve involves turning the handwheel to move the gate up or down on the stem. This motion opens or closes the valve, allowing for unobstructed passage or blocking the flow of media. Unlike quarter-turn valves, gate valves require multiple turns to fully open or close, making them suitable for applications that do not require frequent adjustments to flow.
Advantages of Using a Gate Valve
One of the main advantages of gate valves is the minimal pressure loss they induce due to their straight-through unobstructed passageway. This design also allows for the passage of pigs during pipe cleaning procedures. Additionally, gate valves are cost-effective when operated manually and are suitable for applications where flow regulation is not required.
Limitations and Considerations for Gate Valves
While gate valves offer advantages, they also have limitations. They are slower to operate compared to other types of valves and should only be used in fully open or closed positions to avoid damage. Careful consideration of the specific application, including factors such as flow control requirements and frequency of operation, is essential when deciding whether to use gate valves.
By understanding the basic structure, mechanics of operation, advantages, and limitations of gate valves, engineers and system designers can make informed choices about the suitability of gate valves for different fluid control applications.
Exploring Ball Valves
Ball Valve Design and Components
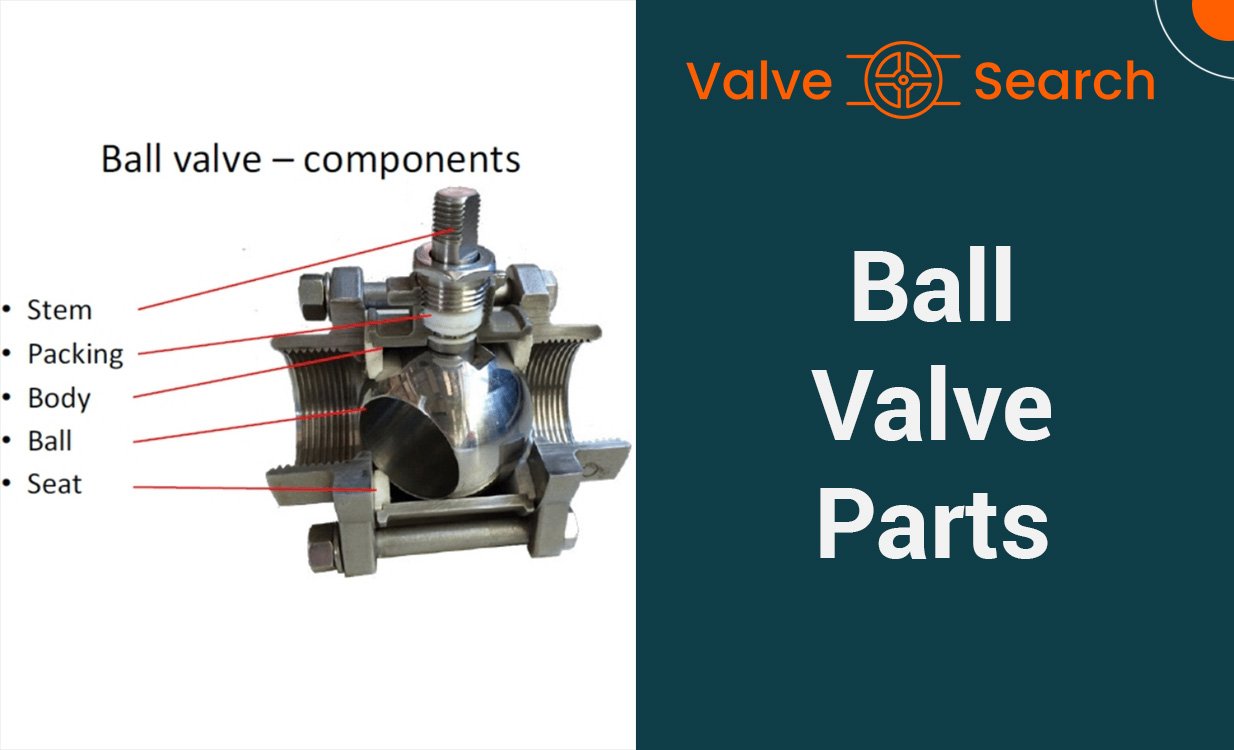
Ball valves are designed with a hollow, perforated, and pivoting ball to control the flow of fluid through them. The primary components of a ball valve include the ball, stem, body, and seats. The ball has a hole through the middle, allowing fluid to pass when the hole is in line with the flow. As the ball rotates 90 degrees, the hole becomes perpendicular to the flow, stopping the circulation of the fluid.
The Functionality of Ball Valves
Ball valves are known for their exceptional shut-off functionality, as they provide a secure seal even after extended periods of inactivity. Their quick quarter-turn operation allows for swift and complete shut-off, reducing the chances of leakage. This functionality makes ball valves ideal for applications requiring tight shut-off and precise control of flow.
Benefits of Choosing Ball Valves
Choosing ball valves offers several advantages. Their durable construction and reliable performance make them suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Additionally, ball valves provide low maintenance requirements due to their simple design and efficient shut-off capability. Furthermore, ball valves are versatile and can be used in various industries, including oil and gas, water and wastewater, chemical, and petrochemical industries.
Potential Drawbacks of Ball Valves
While ball valves offer numerous benefits, they also have potential drawbacks. One primary drawback is the limited throttling capabilities of ball valves. Unlike globe valves, which offer finer control of flow, ball valves are better suited for full-open or full-closed applications. Additionally, the initial cost of ball valves can be higher compared to other valve types, which may impact budget considerations during the selection process.
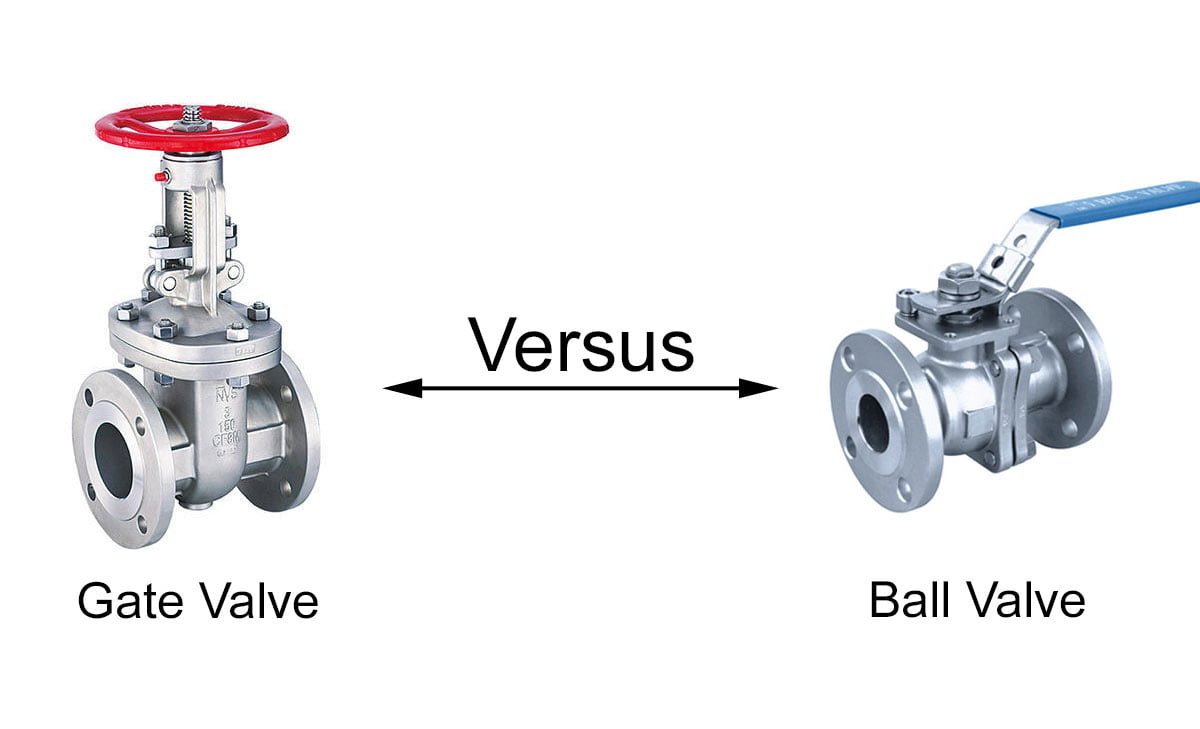
Key Differences Between a Gate Valve and a Ball Valve
The distinctions between gate valves and ball valves are vital for understanding their unique operational characteristics and suitability for specific applications.
Operational Speed and Application
Ball valves are designed for swift operation, employing a quarter turn (90°) of the handle to quickly open or close the valve. This rapid shut-off mechanism makes ball valves ideal for applications requiring immediate flow control adjustments, such as in emergency shut-off systems.
In contrast, gate valves operate at a slower pace, necessitating more than a full 360° turn to close the valve. This gradual shut-off capability is advantageous in scenarios where water hammer needs to be minimized, as the slower opening and closing motion helps mitigate pressure surges and associated risks.
Flow Control Capabilities
The distinct shut-off mechanisms of ball valves and gate valves influence their flow control capabilities. Ball valves offer efficient flow regulation with their swift operation, making them suitable for on/off control of fluid and gas flow.
On the other hand, the slower shut-off process of gate valves enables precise flow adjustments, permitting fine-tuning of the flow rate to meet specific system requirements. This capability makes gate valves well-suited for applications where precise flow control is essential.
Pressure and Temperature Tolerance
Ball valves and gate valves exhibit differences in their pressure and temperature tolerance levels. Ball valves, with their quick-acting design, are susceptible to generating water hammer due to the rapid opening and closing, making them less suitable for high-pressure systems. However, they are well-suited for a wide range of temperature conditions.
In contrast, the slower operation of gate valves reduces the risk of water hammer, making them a favorable choice for high-pressure environments. Gate valves also demonstrate robust performance across a spectrum of temperature conditions, enhancing their suitability for applications involving fluctuating temperature ranges.
The operational disparities between gate valves and ball valves underscore the importance of selecting the most appropriate valve type to optimize system performance and reliability.
Selecting the Right Valve for Your Needs – Ball or Gate Valve
Valves play a crucial role in controlling the flow of liquids and gases in various processes and systems. However, choosing the right valve can be a complex task. Several factors influence valve selection, including the specific application requirements for gate valves and ball valves.
Factors Influencing Valve Selection
When selecting a valve, it’s essential to consider the following factors:
- System performance requirements
- Valve type and size based on functions such as shut off, diversion, mixing, relief, and adjustment of flow
- Materials of construction and chemical compatibility
- Performance requirements such as pressure and temperature ranges
- Special requirements for check valves, including response time and cracking pressure
Specific Applications for a Gate Valve
Gate valves are suitable for various applications, including:
- On/Off control for straight-line flow
- Full flow or no flow applications
- Well-suited for high-pressure systems
- Not ideal for throttling or regulating flow due to potential erosion of the gate and seat
Specific Applications for a Ball Valve
Ball valves are well-suited for specific applications, including:
- On/Off control for straight-line flow
- Quick opening and closing with minimal friction loss
- Ideal for high-pressure, high-temperature, and corrosive fluid applications
- Limited use in throttling applications due to potential seat damage
Understanding the specific applications for gate valves and ball valves enables informed decision-making when it comes to selecting the right valve for your needs.
Maintenance and Durability of Gate and Ball Valves
When considering the selection of valves for industrial applications, it is crucial to evaluate their maintenance requirements, durability, and lifespan. Both gate and ball valves play integral roles in controlling the flow of gas or fluid media within various systems. Understanding the maintenance protocols and durability comparisons between these valve types is essential for ensuring optimal performance.
Maintenance Requirements
Gate Valve
Gate valves necessitate periodic maintenance due to their design, which is susceptible to debris accumulation that can hinder proper operation. Regular inspections and cleaning of the valve components are imperative to prevent potential blockages and ensure smooth functionality. Additionally, lubrication of the gate valve stem and seating surfaces is recommended to minimize wear and maintain sealing integrity.
Ball Valve
Ball valves are relatively low-maintenance, often designed for maintenance-free operation throughout their lifespan. However, periodic inspections to check for wear on the ball and seats, as well as ensuring proper functioning of the actuator or handle, are essential for prolonged longevity and optimal performance.
Durability and Lifespan Comparisons
Gate Valve
Gate valves are known for their robust construction, making them suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. With proper maintenance, gate valves can exhibit extended durability, providing reliable service over an extended lifespan. However, their susceptibility to internal damage from debris and sediment accumulation may impact their overall longevity.
Ball Valve
Ball valves are recognized for their durability in high-pressure and high-volume applications, offering resistance to corrosion and wear. Their simple yet sturdy construction contributes to prolonged lifespan and minimal maintenance requirements. With proper care and adherence to preventive measures, ball valves can ensure consistent performance and longevity in diverse industrial environments.
In conclusion, understanding the maintenance needs and durability aspects of gate and ball valves is vital for informed decision-making in valve selection. Implementing proactive maintenance practices and considering the specific operational requirements of the system can significantly contribute to the extended lifespan and reliable performance of these essential components.
Cost Implications and Availability
When comparing gate valves and ball valves, the cost implications and availability are critical factors to consider. Let’s delve into the cost comparison of gate and ball valves, along with the availability and sourcing considerations.
Cost Comparison of Gate and Ball Valves
In terms of cost, gate valves are generally more economical than ball valves. Gate valves are simpler in design, consisting of fewer parts, which often leads to a lower purchase price. Additionally, their straightforward construction makes them easier and more cost-effective to maintain in the long run. On the other hand, ball valves are slightly more expensive due to their complex design and the precision required in manufacturing. It’s important to weigh the initial cost against the long-term maintenance expenses when deciding between the two.
Availability and Sourcing Considerations
The availability of gate and ball valves can vary based on factors such as size, pressure rating, and material of construction. Both types of valves are widely available in the market, but the specific requirements of a project or application can impact their availability. When sourcing these valves, it’s crucial to consider lead times, supplier reliability, and the potential for customization. Additionally, evaluating the compatibility of the valves with existing systems and the ease of installation can influence the overall availability and sourcing decisions.
In conclusion, while gate valves may offer cost advantages, the availability and sourcing considerations for both gate and ball valves play a significant role in determining the most suitable option for a given application or project.
Conclusion on Gate Valve vs. Ball Valve
In conclusion, the choice between gate valves and ball valves depends on the specific requirements of your application. Gate valves are better suited for situations that require a complete shutoff, while ball valves offer faster operation and are ideal for applications where quick cycle times are essential. Understanding the structural and operational variances between the two valve types is crucial in selecting the right valve for your particular needs. Each valve has its own advantages and limitations, and making an informed decision based on these factors is essential for optimal performance and longevity of your system.