High Pressure Gate Valves: Comprehensive Technical Guide

Table of Contents
ToggleA Comprehensive Technical Guide to High Pressure Gate Valves
When it comes to managing fluid flow in industrial systems, the high-pressure gate valve is a critical component that can significantly impact performance and reliability. In this comprehensive technical guide, we will delve into the intricate details and applications of high-pressure gate valves, shedding light on their essential role in fluid dynamics. Whether you are seeking to enhance your expertise or revolutionize your approach to industrial challenges, this guide is an indispensable resource for understanding and utilizing high-pressure gate valves effectively. So, let’s explore the fundamental aspects and practical applications of high-pressure gate valves to elevate your understanding and utilization of this vital industrial component.
Understanding High Pressure Gate Valves
High pressure gate valves are crucial components in industries that handle corrosive fluids and gases. Understanding their definition, basic function, importance in industrial applications, and comparison with other valve types is essential for making informed decisions in selecting the correct high pressure valve.
What is a High Pressure Gate Valve?
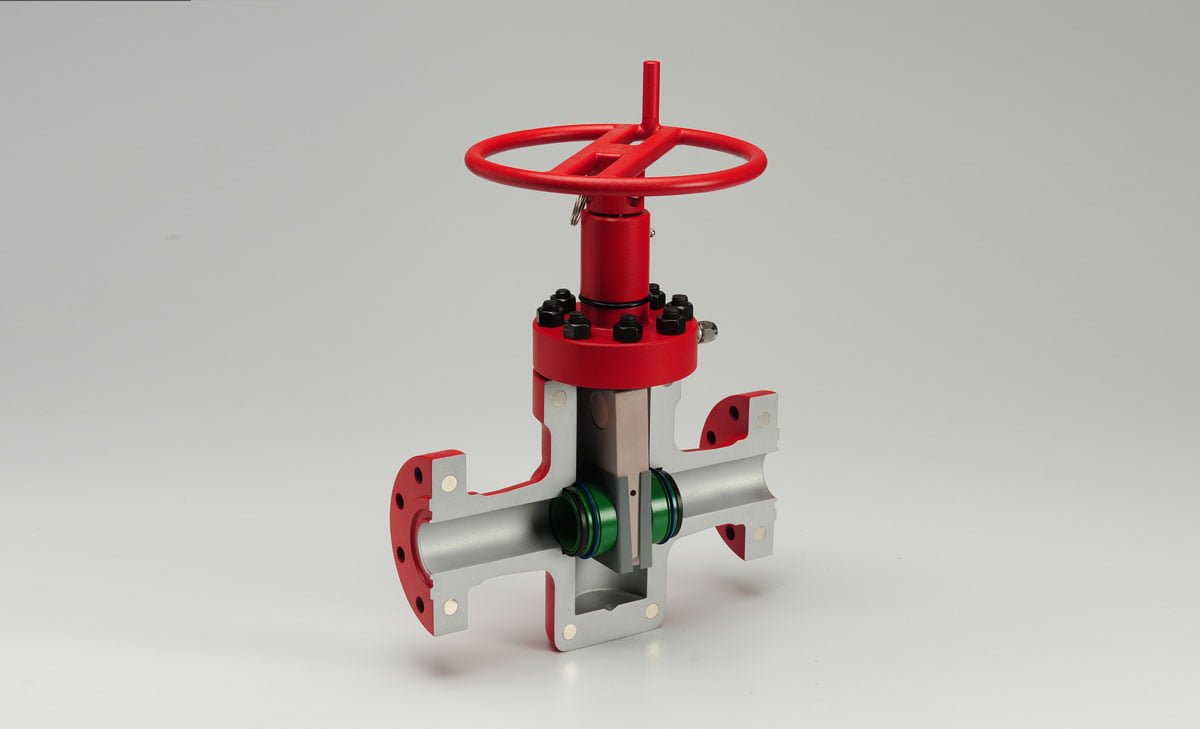
High pressure gate valves are specifically designed to withstand elevated pressure and temperature, making them suitable for applications involving corrosive fluids and gases. These valves consist of various components including the body, stem, disc, seat, and actuator. The body is typically constructed from materials such as stainless steel or titanium to endure high pressure and temperature. The disc regulates the flow of fluid or gas, while the seat ensures a tight seal when the valve is closed. The stem connects the disc to the actuator, which is responsible for opening and closing the valve.
Construction:
The high-pressure gate valve typically features a robust and sturdy construction, with a body, bonnet, gate, seat, and stem made from high-strength materials such as carbon steel, alloy steel, or stainless steel to withstand high pressures and temperatures.
Function:
This type of valve operates by raising and lowering a gate (a solid wedge or parallel disc) to control the flow of fluids. When fully open, the gate creates a straight-through path to minimize pressure drop, and when fully closed, it provides a tight seal to stop the flow completely.
Application:
High-pressure gate valves are crucial components in pipelines, processing plants, and other high-pressure systems where precise flow control and shut-off capabilities are required to ensure safe and efficient operations.
Key Features:
These valves are designed to handle pressures ranging from 600 psi to 10,000 psi and above, with sizes varying from 2 inches to 36 inches or larger. They are often equipped with rising stems, non-rising handwheels, and renewable or welded seats for extended service life in demanding environments.
Maintenance and Considerations:
Regular maintenance and inspection are essential to ensure the proper functioning of high-pressure gate valves, including lubrication of moving parts, checking for wear or damage, and addressing any leaks or malfunctions promptly to prevent costly downtime and safety hazards.
Importance in Industrial Applications
High pressure gate valves play a vital role in numerous industrial applications, including oil and gas, chemical processing, water treatment, and more. Their ability to withstand high pressure and control the flow of corrosive materials makes them indispensable for ensuring the safety and efficiency of industrial processes.
Comparison with Other Valve Types
In contrast to other valve types such as ball, globe, and check valves, high pressure gate valves are specifically designed to provide efficient shut-off capabilities in high-pressure applications. While ball valves are known for their tight seal and ease of operation, check valves allow flow in one direction only, and globe valves regulate flow with linear motion. High pressure gate valves, with their wedge-shaped disc, are particularly effective for shutting off the flow in high-pressure situations, making them an ideal choice for applications that demand reliable shut-off mechanisms.
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of high pressure gate valves, including their definition, basic function, industrial significance, and comparison with other valve types, is crucial for anyone tasked with selecting the appropriate valve for high-pressure applications.

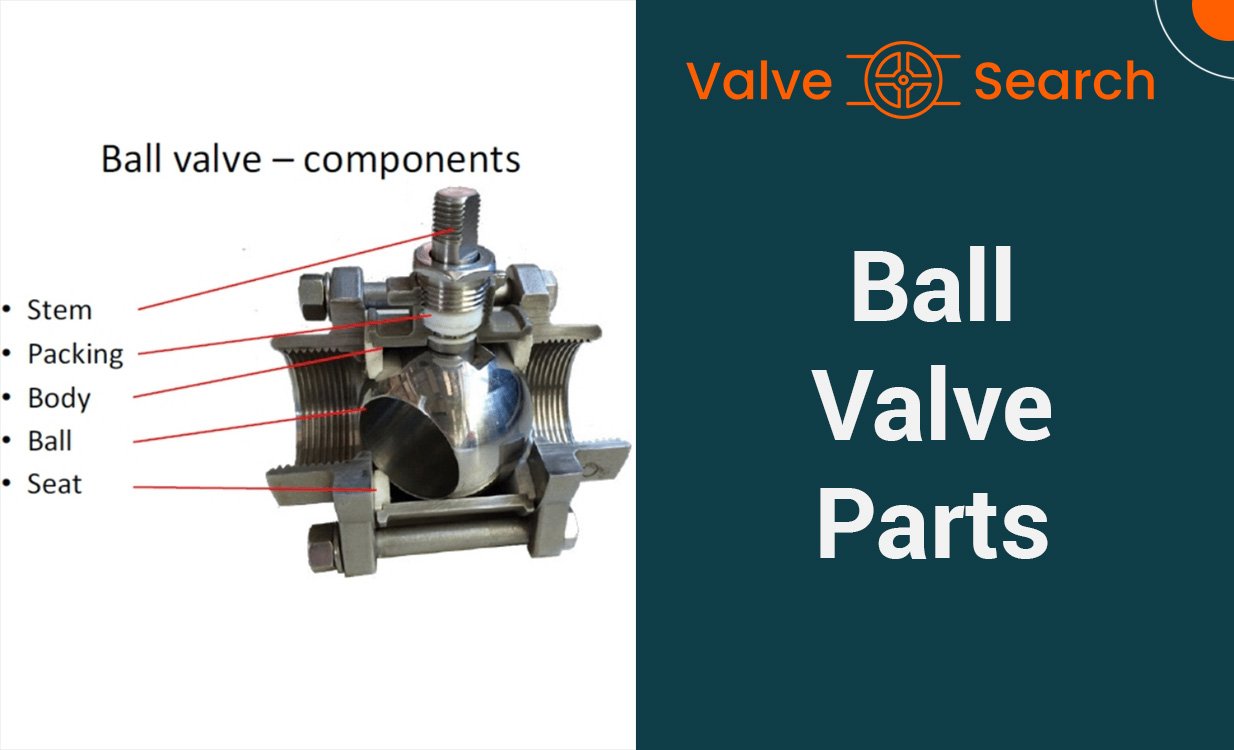
Components of a High Pressure Gate Valve
Gate valves are crucial components in industrial operations, allowing or restricting flow with a simple up or down motion of a gate. Understanding the key components of high pressure gate valves is essential for their effective use and maintenance. Below, we delve into the main elements that make up a high pressure gate valve, providing insights into their functions and variations.
The Body
The body of a high pressure gate valve is the primary pressure-containing structure, housing key operational components such as the gate and seat. It is responsible for facilitating the flow through the valve and is typically linked to the piping on both ends. The connection type, including threaded, flange, butt weld, compression fitting, or tube fitting, should align with client specifications, valve size, and operating pressure for optimal performance.
The Bonnet
A crucial pressure-containing part, the bonnet encloses and protects the valve’s stem and gate. Its design allows for access to internal components for repair or maintenance purposes. Various types of body-bonnet connections are available, each offering unique advantages based on the size of the gate valve and the operational pressure requirements.
- Screwed Bonnet: This simple connection provides quick access but is limited to small gate valves and low-pressure applications, offering a long-lasting, leak-proof seal and easy disassembly.
- Union Bonnet: Featuring a more robust design with a union nut that prevents seal deterioration over time, it is suitable for applications requiring frequent bonnet removal.
- Bolted Bonnet: Ideal for larger valve sizes and higher working pressures, this robust connection utilizes flanges and bolts, requiring a gasket to seal the body-bonnet joint.
- Welded Bonnet: Suited for designs where disassembly is not required, providing a lighter assembly than the bolted bonnet within the same pressure range.
- Pressure Seal Bonnet: Specifically designed for high-pressure applications exceeding 1,500 psi, utilizing the operational pressure to enhance the body-bonnet joint seal.
The Gate
The gate, also known as a disc or obturator, is responsible for regulating the flow through the valve. Various gate designs and technologies are available, catering to different application requirements.
- Wedge Gate: This common design features a wedge-shaped disc that obstructs or allows flow by sitting or rising from inclined seats. It is particularly suitable for high flow or turbulent applications, such as steam services, with minimal frictional seat wear under high differential pressures.
The Seat
The seat provides a sealing surface for the gate, ensuring a tight shutoff and preventing leakage. It is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the valve’s closure, especially under high pressure conditions.
The Stem
The stem facilitates the up and down movement of the gate, connecting the actuator to the gate itself. It plays a vital role in ensuring precise control over the gate’s position, allowing for efficient flow regulation in high pressure environments.
Understanding the intricate components of high pressure gate valves is essential for their proper selection, installation, and maintenance in industrial applications. By comprehensively exploring the body, bonnet, gate, stem, and seat of these valves, one can gain valuable insights into their functionalities and variations, empowering informed decision-making for optimal operational performance.
Types of High Pressure Gate Valves
When it comes to controlling high pressure fluid flow, gate valves are essential components. Different types of gate valves are designed to handle various pressure levels and flow requirements. Understanding the specific types of high pressure gate valves can help you make informed decisions for your industrial applications.
Here there are several types of high pressure gate valves, each with unique features and uses:
- Rising Stem Gate Valves: These valves are equipped with a stem that rises as the valve is opened, providing a visual indication of the valve’s position. They are commonly used in high pressure systems where accurate flow control is crucial.
- Non-Rising Stem Gate Valves: Unlike rising stem gate valves, the stem of these valves does not rise as the valve is opened or closed. They are suitable for high pressure applications where space is limited, as they do not require as much vertical space for operation.
- Wedge Gate Valves: This type of gate valve features a wedge-shaped gate that provides a tight seal against the valve seats, making it ideal for high pressure environments. Wedge gate valves are available in various configurations, including solid wedge, flexible wedge, and split wedge designs.
- Parallel Slide Gate Valves: Parallel slide gate valves are designed to minimize friction between the gate and seats during operation, making them well-suited for high pressure and high temperature applications. They offer excellent sealing capabilities and are often used in steam and power generation systems.
- Slab Gate Valves: Slab gate valves are specifically engineered to withstand extreme pressure and temperature conditions. The flat gate design ensures a tight seal, making them a reliable choice for critical high pressure applications in the oil and gas industry.
- Through-Conduit Gate Valves: These valves feature a full-bore design with a smooth flow path, allowing unobstructed passage of fluids. Through-conduit gate valves are preferred for high pressure and high velocity applications, offering minimal pressure drop and reduced turbulence.
- Expanding Gate Valves: Designed for high pressure and high temperature service, expanding gate valves utilize a mechanism that expands the gate as it moves across the seats to ensure a tight seal. This design is effective in preventing leakage in demanding operating conditions.
- Pressure Seal Gate Valves: Pressure seal gate valves are specifically engineered to handle high pressure applications. They feature a unique pressure seal bonnet design that enhances the valve’s ability to contain pressure, making them suitable for severe service conditions.
The selection of the right type of high pressure gate valve is crucial for maintaining the integrity and efficiency of industrial fluid systems. By understanding the characteristics and capabilities of different gate valve types, you can make informed choices that align with the requirements of your specific high pressure applications.
Solid Wedge Valves
Solid wedge valves are known for their simple yet robust design. They are ideal for high-pressure applications where the flow of fluid needs to be completely shut off. The solid wedge design provides a tight seal, making these valves suitable for systems handling abrasive and corrosive fluids.
Flexible Wedge Valves
Flexible wedge valves feature a two-piece disc that flexes to accommodate changes in the seating stress caused by temperature fluctuations. This design minimizes the risk of leakage in high-pressure environments. Flexible wedge valves are commonly used in industries where the temperature differentials are significant.
Split Wedge or Parallel Disk Valves
Split wedge or parallel disk valves are designed to minimize the effects of thermal binding in high-pressure systems. The parallel disc design allows for efficient operation even in conditions where thermal expansion and contraction could affect valve performance. These valves are suitable for applications where temperature variations are a concern.
High pressure gate valves play a critical role in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of high-pressure systems. Understanding the characteristics and applications of different types of high pressure gate valves is essential for selecting the right valve for specific operational requirements.

Image Credit: F&M Armaturen
Materials Used in High Pressure Gate Valves
Selecting the right materials for high pressure gate valves is crucial to ensuring optimal performance and longevity. The choice of materials depends on various factors such as the composition of the media, operating pressure, service temperatures, and material compatibility. Additionally, standards set by organizations like the American Petroleum Institute (API) and the National Association for Corrosion Engineers (NACE) play a significant role in material selection for specific environments.
Cast Iron and Its Alloys
High pressure gate valves often utilize cast iron and its alloys for their robustness and ability to withstand varying operating conditions. Cast iron gate valves are known for their durability and resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for applications involving abrasive or corrosive media. These valves are widely used in industries such as oil and gas, wastewater treatment, and chemical processing.
Stainless Steel Varieties
Stainless steel gate valves are favored for their corrosion resistance and strength, making them suitable for high pressure applications where exposure to harsh chemicals or extreme temperatures is a concern. The versatility of stainless steel allows for the adaptation of gate valves to a wide range of demanding environments, including marine, pharmaceutical, and petrochemical industries.
Exotic Alloys for Extreme Conditions
In environments with extreme operating conditions, such as high temperatures, pressure differentials, or exposure to aggressive media, high pressure gate valves may employ exotic alloys like Hastelloy, Inconel, or Monel. These alloys offer exceptional resistance to corrosion, erosion, and thermal degradation, making them essential for critical applications in aerospace, power generation, and industrial processing.
PVC gate valve features
- PVC gate valves are not damaged by freezing temperatures, making them suitable for cold climate applications.
- The lightweight nature of PVC gate valves makes them easy to handle and install.
- PVC gate valves exhibit excellent chemical resistance, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of media.
Operation of High Pressure Gate Valves
High-pressure gate valves play a crucial role in many industrial applications. Understanding their operation is essential for ensuring efficient and reliable performance. Two primary methods are employed in operating high-pressure gate valves: manual operation and automated valve actuators.
Manual Operated Valves
Manual operation of high-pressure gate valves involves the use of a handwheel or a manual lever to control the opening and closing of the valve. By manually rotating the handwheel or the lever, the position of the gate is adjusted, allowing for the regulation of fluid flow. This method provides the operator with direct control over the valve and is often used in applications where precise adjustments are required.
Automated Valve Actuators
In contrast, automated valve actuators are utilized to mechanize the operation of high-pressure gate valves. These actuators can be electrically, pneumatically, or hydraulically powered, providing a more efficient and automated means of controlling the valve. Automated actuators are ideal for applications where remote operation, frequent adjustments, or precise flow control are necessary.
The selection of the most suitable operation method depends on the specific requirements of the industrial process, including the need for manual intervention, the frequency of adjustments, and the level of precision required in regulating fluid flow. Whether manual or automated, the operation of high-pressure gate valves is pivotal in ensuring optimal performance and seamless functionality within high-pressure systems.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper Installation Techniques
When installing a high-pressure gate valve, it is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines meticulously. Ensure that the valve is positioned correctly and that all the necessary equipment, such as flanges and gaskets, are in place. Proper torquing of fasteners is essential to prevent leakage under high pressure. It’s imperative to verify that the valve’s orientation matches the flow direction specified by the manufacturer to guarantee optimal performance.
Routine Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance is key to ensuring the longevity and efficiency of high-pressure gate valves. This includes periodic inspections for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Lubrication of the valve components should be performed according to the manufacturer’s recommendations to maintain smooth operation. Additionally, monitoring the valve’s performance and addressing any irregularities promptly can help prevent potential issues from escalating.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common issues with high-pressure gate valves may include leaking, difficulty in operation, or reduced flow capacity. In the event of leakage, it is important to identify the source and address it immediately. Difficulties in operation could be due to internal components seizing or misalignment, which may require thorough assessment and potential replacement. Reduced flow capacity might be attributed to obstructions, and inspecting the valve’s internals can help pinpoint the cause for remediation. Regular monitoring and swift resolution of these issues are essential to maintain the valve’s functionality under high-pressure conditions.
Applications of High Pressure Gate Valves
High pressure gate valves are utilized in various industries due to their reliability and durability. Their ability to control high-pressure fluids and gases makes them indispensable in critical applications. Let’s explore the key industries where high pressure gate valves play a vital role:
Oil and Gas Industry
In the oil and gas sector, high pressure gate valves are essential components in wellheads, manifolds, and pipelines. They are employed to regulate the flow of crude oil, natural gas, and refined products. These valves ensure uninterrupted operation under extreme pressure and harsh environments, contributing to the efficient and safe extraction, processing, and transportation of oil and gas resources.
Power Generation
High pressure gate valves are integral to power generation facilities, where they are deployed in steam systems and feedwater control applications. These valves play a crucial role in maintaining optimal operating conditions and safety within high-pressure steam environments, ensuring continuous and reliable electricity generation.
Water and Wastewater Management
In the water and wastewater treatment industry, high pressure gate valves are utilized in critical processes such as desalination, filtration, and water distribution systems. These valves enable precise control of high-pressure water and wastewater flows, facilitating efficient and sustainable management of water resources and treatment processes.
Chemical Processing
Within the chemical processing industry, high pressure gate valves are employed in various applications, including refining, petrochemical production, and chemical transportation systems. These valves ensure the safe and precise regulation of high-pressure chemical substances, contributing to the efficient and secure operation of chemical processing plants and distribution networks.
High pressure gate valves play a crucial role in these diverse industries, ensuring the seamless control of high-pressure fluids and gases in demanding operational environments. Their reliability and robustness make them indispensable components in critical applications, contributing to the safety, efficiency, and sustainability of industrial operations.

Selecting the Right High Pressure Gate Valve
When selecting a high-pressure gate valve, it is crucial to consider various factors to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Identifying the correct size and type, understanding pressure and temperature ratings, and evaluating media compatibility are all essential aspects of making the right choice.
Identifying the Correct Size and Type
High-pressure gate valves come in various sizes and types to suit different applications. It’s important to consider the dimensions of the pipeline or system where the valve will be installed. Factors such as flow rate, pressure, and the nature of the media being controlled will influence the choice of size and type. Additionally, the operating conditions and space constraints should be taken into account when determining the most suitable size and type of gate valve for a specific application.
Pressure and Temperature Ratings
High-pressure gate valves are designed to withstand demanding operating conditions. Understanding the pressure and temperature ratings is crucial to ensuring the valve can perform effectively and safely within the intended environment. The valve’s pressure rating should exceed the maximum operating pressure expected in the system, while the temperature rating should align with the range of temperatures the valve will encounter during operation. It’s imperative to select a gate valve with pressure and temperature ratings that align with the specific requirements of the application.
Media Compatibility
The compatibility of the valve with the media it will handle is a critical consideration. Different materials used in high-pressure gate valves may react differently to various media, such as corrosive chemicals or high-temperature fluids. Evaluating the compatibility of the valve materials with the media it will come into contact with is essential to prevent corrosion, degradation, or malfunction. Factors such as chemical composition, pH levels, and abrasive properties of the media should be thoroughly analyzed to select a gate valve that is compatible with the intended application.
In conclusion, selecting the right high-pressure gate valve involves a careful assessment of size, type, pressure and temperature ratings, and media compatibility. By thoroughly considering these factors, it is possible to make an informed decision that ensures the gate valve will meet the specific requirements of the application and deliver reliable performance under high-pressure conditions.
Safety and Regulatory Considerations
Ensuring the operational safety of high-pressure gate valves involves compliance with industry standards, certifications, and regulatory requirements. Adequate understanding and adherence to these guidelines are crucial in maintaining the safety and reliability of these critical components.
Industry Standards and Certifications
High-pressure gate valves must meet specific industry standards and certifications to ensure their performance and safety. The American Petroleum Institute (API) sets standards for various aspects of valve design, production, and testing, including API 600 for steel gate valves and API 602 for compact steel gate valves. Additionally, the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) standards, such as ASME B16.34, provide guidance on valve materials, pressure-temperature ratings, and design validation.
These standards outline rigorous testing, material requirements, and quality control measures that gate valves must undergo to achieve certification. Products that meet these standards bear markings signifying compliance, providing assurance of quality and safety.
Ensuring Operational Safety
Incorporating high-pressure gate valves in industrial processes necessitates a comprehensive approach to operational safety. It involves implementing proper installation, regular maintenance, and adherence to operational guidelines. Employing qualified personnel for installation and maintenance is essential to ensure the valves function optimally under high-pressure conditions.
Furthermore, operational safety encompasses robust risk assessment and mitigation strategies. This involves identifying potential failure points, implementing emergency shutdown procedures, and ensuring the availability of pressure relief mechanisms to prevent catastrophic incidents.
Adhering to stringent safety protocols, such as lockout-tagout procedures and regular equipment inspections, further enhances operational safety. It is imperative to promote a safety-oriented culture within the organization, emphasizing the importance of vigilance and adherence to safety protocols when working with high-pressure gate valves.
In summary, high-pressure gate valves demand adherence to industry standards, certifications, and rigorous safety protocols to ensure their reliable performance and mitigate operational risks. Appreciating the significance of these considerations is pivotal in safeguarding both personnel and industrial infrastructure.
Conclusion
Understanding the critical role of high pressure gate valves in industrial processes is essential for maximizing efficiency and minimizing downtime. These unassuming yet vital components play a crucial role in controlling the flow of various media within systems.
By exploring the intricacies and applications of gate valves, one can enhance their expertise and potentially revolutionize their approach to fluid dynamics. Gate valves, with their all-or-nothing design, are particularly well-suited for applications requiring a complete stop or full pass-through of fluids, making them indispensable in high-pressure environments.
Recognizing the distinctive parts of a gate valve and understanding their unique purpose is fundamental to ensuring optimal performance in industrial applications.